A group of academics from the New Jersey Institute of Technology (NJIT) has warned of a novel technique that could be used to defeat anonymity protections and identify a unique website visitor.
“An attacker who has complete or partial control over a website can learn whether a specific target (i.e., a unique individual) is browsing the website,” the researchers said. “The attacker knows this target only through a public identifier, such as an email address or a Twitter handle.”
The cache-based targeted de-anonymization attack is a cross-site leak that involves the adversary leveraging a service such as Google Drive, Dropbox, or YouTube to privately share a resource (e.g., image, video, or a YouTube playlist) with the target, followed by embedding the shared resource into the attack website.
This can be achieved by, say, privately sharing the resource with the target using the victim’s email address or the appropriate username associated with the service and then inserting the leaky resource using an <iframe> HTML tag.
In the next step, the attacker tricks the victim into visiting the malicious website and clicking on the aforementioned content, causing the shared resource to be loaded as a pop-under window (as opposed to a pop-up) or a browser tab — a method that’s been used by advertisers to sneakily load ads.
This exploit page, as it’s rendered by the target’s browser, is used to determine if the visitor can access the shared resource, successful access indicating that the visitor is indeed the intended target.
The attack, in a nutshell, aims to unmask the users of a website under the attacker’s control by connecting the list of accounts tied to those individuals with their social media accounts or email addresses through a piece of shared content.
In a hypothetical scenario, a bad actor could share a video hosted on Google Drive with a target’s email address, and follow it up by inserting this video in the lure website. Thus when visitors land on the portal, a successful loading of the video could be used as a yardstick to infer if their victim is one among them.
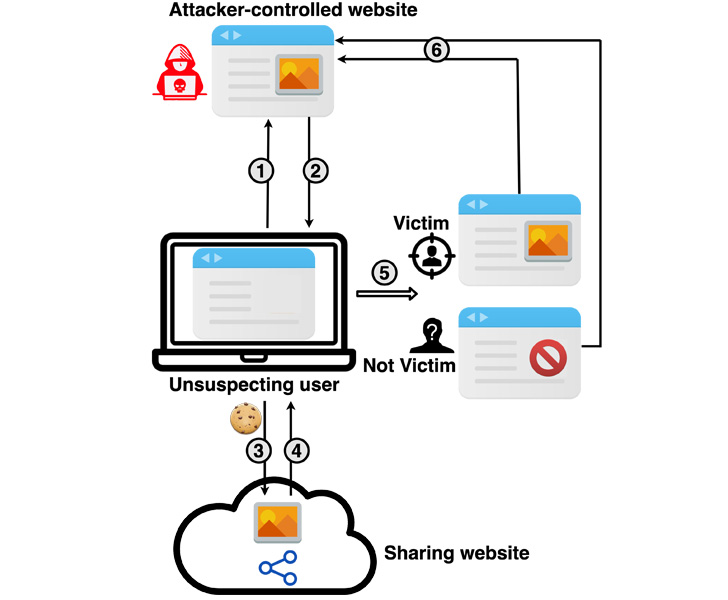
The attacks, which are practical to exploit across desktop and mobile systems with multiple CPU microarchitectures and different web browsers, are made possible by means of a cache-based side channel that’s used to glean if the shared resource has been loaded and therefore distinguish between targeted and non-targeted users.
Put differently, the idea is to observe the subtle timing differences that arise when the shared resource is being accessed by the two sets of users, which, in turn, occurs due to differences in the time it takes to return an appropriate response from the web server depending on the user’s authorization status.
The attacks also take into account a second set of differences on the client-side that happens when the web browser renders the relevant content or error page based on the response received.
“There are two main causes for differences in the observed side channel leakages between targeted and non-targeted users – a server-side timing difference and a client-side rendering difference,” the researchers said.
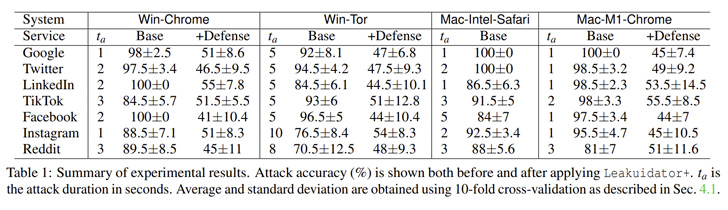
While most popular platforms such as those from Google, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, Twitter, and TikTok were found susceptible, one notable service that’s immune to the attack is Apple iCloud.
It’s worth pointing out the de-anonymization method banks on the prerequisite that the targeted user is already logged in to the service. As mitigations, the researchers have released a browser extension called Leakuidator+ that’s available for Chrome, Firefox, and Tor browsers.
To counter the timing and rendering side channels, website owners are recommended to design web servers to return their responses in constant time, irrespective of whether the user is provisioned to access the shared resource, and make their error pages as similar as possible to the content pages to minimize the attacker-observable differences.
“As an example, if an authorized user was going to be shown a video, the error page for the non-targeted user should also be made to show a video,” the researchers said, adding websites should also be made to require user interaction before rendering content.
“Knowing the precise identity of the person who is currently visiting a website can be the starting point for a range of nefarious targeted activities that can be executed by the operator of that website.”
The findings arrive weeks after researchers from the University of Hamburg, Germany, demonstrated that mobile devices leak identifying information such as passwords and past holiday locations via Wi-Fi probe requests.
In a related development, MIT researchers last month revealed the root cause behind a website fingerprinting attack as not due to signals generated by cache contention (aka a cache-based side channel) but rather due to system interrupts, while showing that interrupt-based side channels can be used to mount a powerful website fingerprinting attack.
Source :
https://thehackernews.com/2022/07/new-cache-side-channel-attack-can-de.html
