3 May 2023
Your site needs to have a defined structure because, without it, it’ll just be a random collection of pages and blog posts. Your users need this structure to navigate on your site, to click from one page to another. Google also uses the structure of your site to determine what content is important and what is less relevant. This guide tells you everything you need to know about site structure.
Table of contents
- Importance for usability
- Importance of your site structure for SEO
- How to set up the structure of your site
- Contextual internal linking
- Landing pages
- Maintaining your site structure
- Internal linking with Yoast SEO
- The importance of site structure
What is site structure, and why is it important?
Site structure refers to organizing and arranging a website’s pages and content. It defines the information hierarchy within the site and serves as a roadmap for search engine crawlers. A well-structured site facilitates easy navigation, enhances user experience, and helps search engines like Google understand and effectively index the site’s content. This, in turn, can improve the site’s performance by making it easier for users to find and engage with the content. Ultimately, an optimized site structure helps achieve higher rankings, more traffic, and better conversion rates.
Importance for usability
The structure of your website significantly impacts the experience for your visitors (UX). If visitors can’t find the products and information they’re looking for, they’ll not likely become regular visitors or customers. In other words, you should help them navigate your site. A good site structure will help with this.
Navigating should be easy. You need to categorize and link your posts and products so they are easy to find. New visitors should be able to grasp what you’re writing about or selling instantly.
Importance of your site structure for SEO
A solid site structure vastly improves your chances of ranking in search engines. There are three main reasons for this:
a. It helps Google ‘understand’ your site
The way you structure your site will give Google vital clues about where to find the most valuable content on your site. It helps search engines understand what your site is mainly about or what you’re selling. A decent site structure also enables search engines to find and index content quickly. A good structure should, therefore, lead to a higher ranking in Google.
b. It prevents you from competing with yourself
On your site, you might have blog posts that are quite similar. If, for example, you write a lot about SEO, you could have multiple blog posts about site structure, each covering a different aspect. Consequently, Google won’t be able to tell which of these pages is the most important, so you’ll be competing with your content for high rankings. You should let Google know which page you think is most important. You need a good internal linking and taxonomy structure to do this, so all those pages can work for you instead of against you.
c. It deals with changes on your website
The products you sell in your shop will likely evolve. So does the content you’re writing. You probably add new product lines as old stock sells out. Or you write new articles that make old ones redundant. You don’t want Google to show outdated products or deleted blog posts, so you need to deal with these kinds of changes in the structure of your site.
Are you struggling with setting up your site’s structure? Don’t know the best strategy to link from one post to another? Check out our Site structure training, part of the Yoast SEO academy. Access to Yoast SEO academy is included in the price of Yoast SEO Premium. Before you know it, you’ll be able to improve your rankings by creating the best structure for your site!
How to set up the structure of your site
So, how do you construct a solid site structure? First, we’ll look at an ideal site structure and then explain how to achieve this for your site.
What’s an ideal site structure?
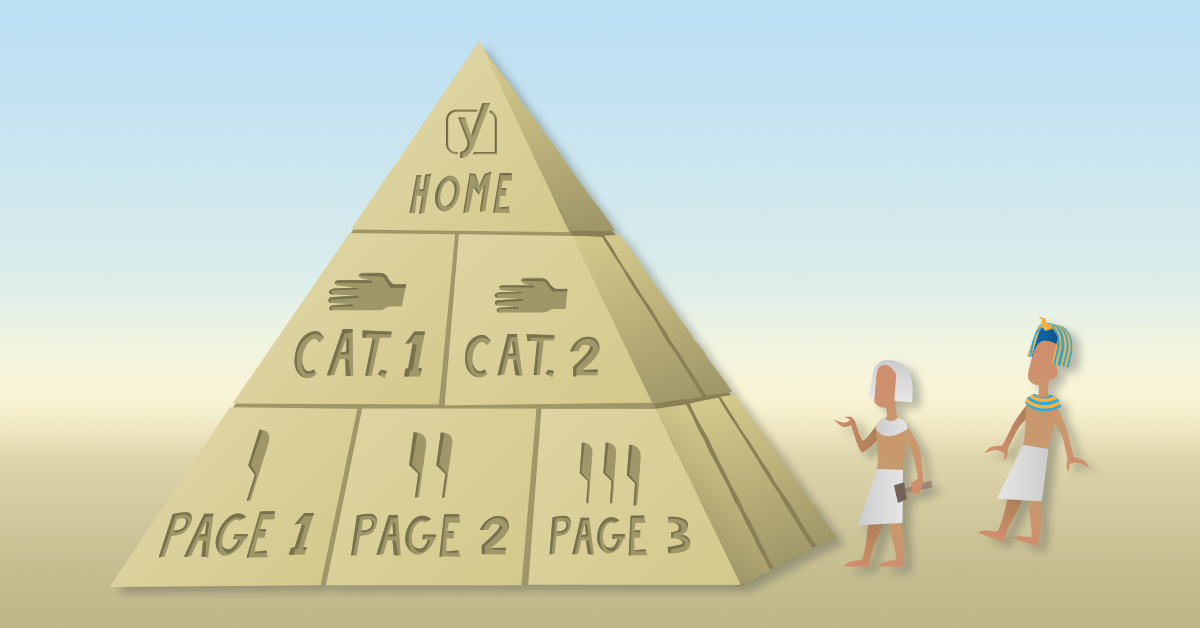
Let’s start by looking at an ideal situation: How should you organize your site if you’re starting from scratch? We think a well-organized website looks like a pyramid with several levels:
- Homepage
- Categories (or sections)
- Subcategories (only for larger sites)
- Individual pages and posts
The homepage should be at the top. Then, you have some sections or category pages beneath it. You should be able to file your content under one of these categories. You can divide these sections or categories into subcategories if your site is larger. Beneath your categories or subcategories are your pages and posts.
Your homepage
On top of the pyramid is the homepage. Your homepage should act as a navigation hub for your visitors. This means, amongst others, that you should link to your most important pages from your homepage. By doing this:
- Your visitors are more likely to end up on the pages you want them to end up on;
- You show Google that these pages are important.
Further down this article, we’ll help you determine which pages are essential to your business.
Beware not to link too many pages from your homepage, which will cause clutter. And a cluttered homepage doesn’t guide your visitors anywhere. If you want to optimize your homepage further, you can do many other things. Read our article on homepage SEO to find out what.
Navigation
In addition to having a well-structured homepage, it’s also important to create a clear navigation path on your site. Your site-wide navigation consists of two main elements: the menu and the breadcrumbs.
The menu
First, let’s take a look at the menu. The website menu is the most common aid for navigation on your website, and you want to make the best possible use of it. Visitors use your menu to find things on your website. It helps them understand the structure of your website. That’s why the main categories on your site should all have a place in the menu on your homepage.
Furthermore, putting everything in just one menu is not always necessary. If you have a big site with lots of categories, this may clutter your website and makes your main menu a poor reflection of the rest of your site. Where it makes sense, creating a second menu is perfectly fine.
For instance, eBay has one menu at the top of the page – also called the top bar menu – and, in addition to that, a main menu. This top bar menu links to important pages that aren’t categories in the shop, like pages that relate to the visitor’s account on the site. The main menu reflects the most important product categories on eBay.

Finally, just like on your homepage, you shouldn’t add too many links to your menu. They will become less valuable for your users and search engines if you do.
Read about optimizing your website’s menu here, or enroll in our site structure training that includes many examples!
Breadcrumb trail
Adding breadcrumbs to your pages can make your site’s structure even clearer. Breadcrumbs are clickable links, usually at the top of a page or post. Breadcrumbs reflect the structure of your site. They help visitors determine where they are on your site. They improve your site’s user experience and SEO, as you can read in our guide on breadcrumbs.
You can use one of the many breadcrumb plugins for your WordPress site. You can also use our Yoast SEO plugin, as we’ve implemented a breadcrumb functionality in our plugin as well.
Taxonomies
WordPress uses so-called taxonomies to group content; other CMSs have similar systems. The word ‘taxonomy’ is a fancy term for a group of things — website pages, in this case — that have something in common. This is convenient because people looking for more information on the same topic can find similar articles more easily. You can group content in different ways. The default taxonomies in WordPress are categories and tags.
Categories
You should divide your site’s blog posts or products into several categories. If these categories grow too big, you should divide these categories into subcategories to clear things up again. For example, if you have a clothing store and sell shoes, you can divide this category into subcategories: ‘boots’, ‘heels’, and ‘flats’. These subcategories contain products, in this case, shoes, of that specific type.
Adding this hierarchy and categorizing your pages helps your user and Google make sense of every page you write. Add your main categories to your site’s menu when implementing your category structure.
Read more: Using category and tag pages for SEO »
Tags
Your site’s structure will also benefit from adding tags. The difference between a category and a tag mostly concerns structure. Categories are hierarchical: you can have subcategories and even sub-subcategories. Tags, however, don’t have that hierarchy. Tags say: “Hey, this article or product has a certain property that might interest a visitor.” Think of it like this: categories are the table of contents of your website, and tags are the index. A tag for the online clothing store mentioned above could be a brand, for instance, Timberlands.
Keep reading: What is the difference between tags and categories? »
Try not to create too many tags. You’re not structuring anything if you add a new unique tag to every post or article. Ensure each tag is used at least twice, and your tags group articles that genuinely belong together.
Some WordPress themes display tags with each post, but some don’t. Ensure your tags are available to visitors somewhere, preferably at the bottom of your article or in the sidebar. Google isn’t the only one that likes tags: they are useful for visitors wanting to read more about the same topic.
Read on: Tagging post properly for users and SEO »
Contextual internal linking
Site structure is all about grouping and linking the content on your site. Until now, we mostly discussed so-called classifying links: links on your homepage, navigation, and taxonomies. On the other hand, contextual links are internal links within the copy on your pages that refer to other pages within your site. For a link to be contextual, the page you link to should be relevant for someone reading the current page. If you look at the previous paragraph, for instance, we link to a post about tagging, so people can learn more about it if they’re interested.
Your most important pages are often very relevant to mention on several pages across your site, so you’ll link to them most often. Just remember that not only the page you’re linking to is relevant, the context of the link is important as well.
Google uses the context of your links to gather information about the page you’re linking to. It always uses the anchor text (or link text) to understand what the page you’re linking to is about. But the anchor text isn’t the only thing Google looks at. Nowadays, it also considers the content around the link to gather extra information. Google is becoming better at recognizing related words and concepts. Adding links from a meaningful context allows Google to value and rank your pages properly. Yoast SEO Premium makes internal linking a breeze by automatically suggesting relevant content from your site to link to.
Contextual linking for blogs
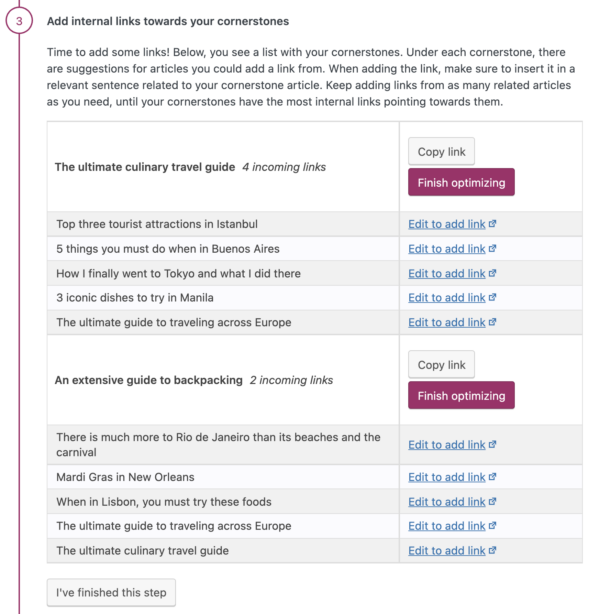
For blogs, you should write extensively on the topics you want to rank for. You should write some main articles — your cornerstone articles — and write various posts about subtopics of that topic. Then link from these related posts to your cornerstone articles and from the cornerstone articles back to related posts. In this way, you’ll ensure that your most important pages have both the most and most relevant links.
The following metaphor might help you understand this principle:
Imagine you’re looking at a map of a state or country. You’ll probably see many small towns and some bigger cities. All towns and cities will be interconnected somehow. You’ll notice that small towns often have roads leading to the big cities. Those cities are your cornerstones, receiving the most links. The small towns are your posts on more specific topics. Some roads (links) lead to these smaller towns, but not as much as the big cities.

Keep on reading: Internal linking why and how »
Contextual linking opportunities for online shops
Contextual internal linking works differently on an online store with very few to no pages that are exclusively meant to inform. You don’t explore a specific topic on your product pages: you’re selling a product. Therefore, on product pages, you mostly want to keep people on a page and convince them to buy the product. Consequently, contextual linking is far less prominent in this context. You generally shouldn’t add contextual links to your product descriptions because it could lead to people clicking away from the page.
There are just a couple of meaningful ways of adding contextual links to the product pages for your ecommerce SEO:
- link from a product bundle page to the individual products
- a ‘related items’ or ‘compare with similar items’ section
- a ‘customers also bought’ section
- a ‘product bundles’ or ‘frequently bought together’ section.
Learn all about setting up a great (internal linking) structure for your online store with our Site structure training, part of our Yoast SEO academy training subscription. We’ve included lots of examples from real websites!
Landing pages
Landing pages are the pages you want your audience to find when they search for specific keywords you’ve optimized for. For instance, we want people who search for ‘free SEO training’ to end up on the page about our free training called ‘SEO for beginners’. You need to approach the content of your most important landing pages differently than your regular pages.
Here, we’ll discuss two types of landing pages: cornerstone pages and product landing pages. They’re both pages you’d like people to land on from the search engines, but they require quite a different approach. But first, we’ll shortly go into search intent because you have to know what your audience is really looking for.
Search intent
When setting up your site structure, you must consider search intent. It’s about what you think people are looking for when they enter a query into a search engine. What do people want to find? And: what do they expect to find?
Consider different possibilities in search intent, as you might want to cater to different types on your site. Are people just looking for an answer to a question or a definition? Are they comparing products before purchase? Or are they intending to buy something right away? This is often reflected in the type of query they make. You can also use Google’s search results to create great content that fits someone’s needs.
When you have an idea of the search intent, ensuring your landing page fits your audience’s search intent is essential. Pages can answer multiple search intents, but you need a clear view of at least your most important pages.
Read all about search intent and why it’s important for SEO.
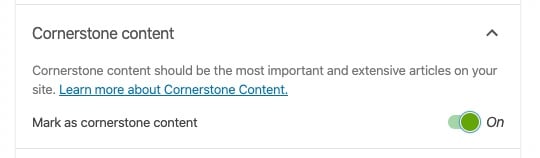
Cornerstone content pages
Cornerstone articles are the most important informational articles on your website. Their focus is to provide the best and most complete information on a particular topic; their main goal is not to sell products.
Because of this focus, we usually think of blogs when discussing cornerstone content. Of course, that doesn’t mean it can only be a blog post. All different kinds of websites have cornerstone articles! Rule of thumb: if an article brings everything you know about a broad topic together, it’s a cornerstone content article.
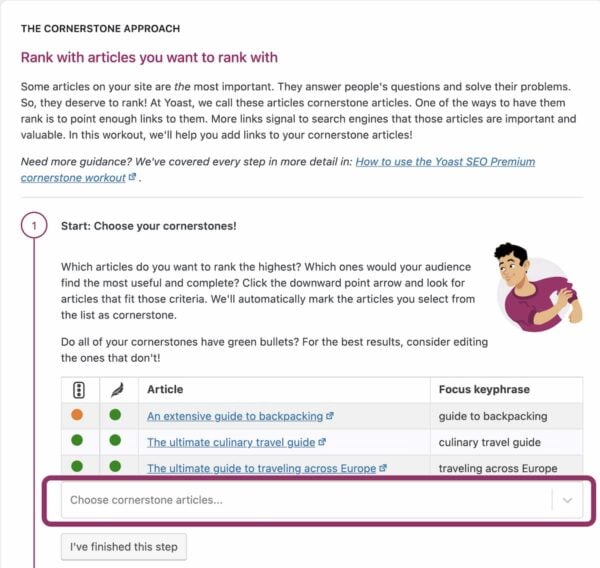
This article explains what cornerstone content is and how to create it. Want to set up your cornerstone content strategy? Our Internal linking SEO workout makes the cornerstone content approach easy to implement!
Product landing pages
Product landing pages significantly differ from cornerstone articles. The latter are lengthy, whereas product landing pages shouldn’t be that long. Rather than complete articles, they should be focused. These pages only need to show what your visitors need to know to be convinced. They don’t need to hold all the information.
You want to rank with these pages, meaning they need content. Enough content for Google to understand what the page is about and what keyword it should rank for. Where cornerstone articles could be made up of thousands of words, a couple of hundred could be enough for product landing pages. The main focus of the content should be on your products.
Michiel listed all the essentials of your product landing page here.
Maintaining your site structure
Structuring or restructuring your content doesn’t always have high priority in everything you have to do. Especially when you blog a lot or add other content regularly, it might feel like a chore. Although it isn’t always fun, you must do it, or your website might become messy. To prevent that from happening, you need to fix your site structure and keep an eye on it while adding new content. Site structure should be part of your long-term SEO strategy.
Evaluate your menu
When your business goal or website changes, your menu must also change. Planning things visually will pay off when you start thinking about restructuring your site. Make a flowchart.
Start with your new menu one or two levels deep and see if you can fit in more pages you have created over the years. You’ll find that some pages are still valid but don’t seem relevant to your menu anymore. No problem, just be sure to link to them on related pages and in your sitemaps so that Google and your visitors can still find these pages. The flowchart will also show you any gaps in the site structure.
Read more: Optimizing your website menu »
Rethink your taxonomy
Creating an overview of your categories, subcategories, and products or posts will also help you to rethink your site’s taxonomy. This could be a simple spreadsheet, but you can use more visual tools like LucidChart or MindNode.
Do your product categories and subcategories provide a logical overview of your product range or your posts and pages? Perhaps you’ve noticed somewhere down the line that one category has been far more successful than others, or you wrote many blog posts on one subject and very few on others.
If one category grows much larger than others, your site’s pyramid could be thrown off balance. Think about splitting this category into different categories. But, if some product lines end up much smaller than others, you might want to merge them. Don’t forget to redirect the ones you delete.
If you have built your HTML sitemap manually, update that sitemap after changing your site structure. In the far more likely event you have an XML sitemap, re-submit it to Google Search Console.
Keep reading: The structure of a growing blog »
Clean up outdated content
You might be able to update and republish some outdated articles to make them relevant again. If an article is outdated, but no one reads it anyway, you might delete it. This could clean up your site nicely.
What you should know, in that case, is that you should never delete a page or article without thinking. If Google cannot find the page, it serves your user a 404 error page. Both the search engine and your visitor will see this error message saying the page doesn’t exist, and that is a bad experience and, thus, bad for your SEO.
Be smart about this! You need to redirect the URL of the page you’re deleting properly so your user (and Google) lands on a different page that is relevant to them. That could even improve your SEO!
Got some old content to clean up on your site? Sort out hidden pages and dead ends in four easy steps with our orphaned content SEO workout, available in Yoast SEO Premium.
Avoid keyword cannibalization
Your website is about a specific topic, which could be quite broad or rather specific. While adding content, you should be aware of keyword cannibalization. If you optimize your articles for keywords that are all too similar, you’ll be devouring your chances of ranking in Google. If you optimize different articles for similar key terms, you’ll be competing with yourself, making both pages rank lower.
You’ll have some work to do if you suffer from keyword cannibalization. In short, you should research the performance of your content and probably merge and redirect some of it. When merging posts, we recommend creating a new draft by cloning one of the original posts with the free Yoast Duplicate Post plugin. This allows you to work on your merged post without making these changes to a live post. Read the guide by Joost to learn more about keyword cannibalization and how to fix it.
Internal linking with Yoast SEO
Feeling a bit overwhelmed by all this advice? Yoast SEO has some handy tools to make internal linking so much easier.
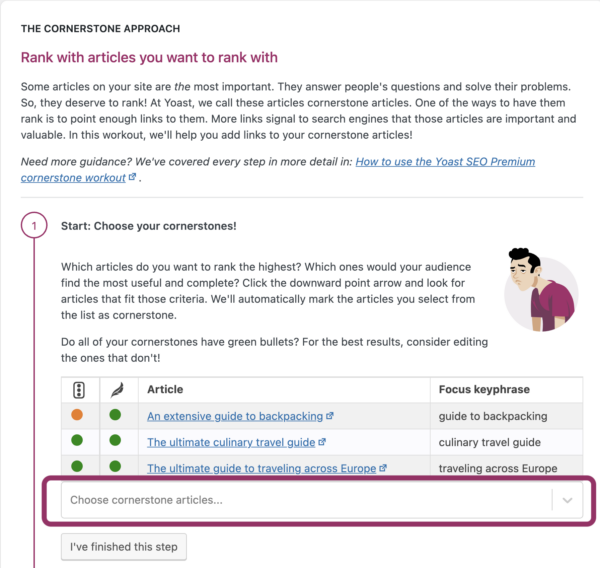
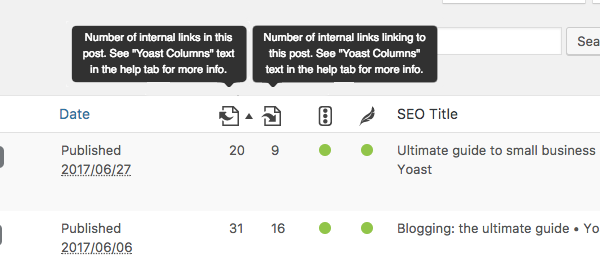
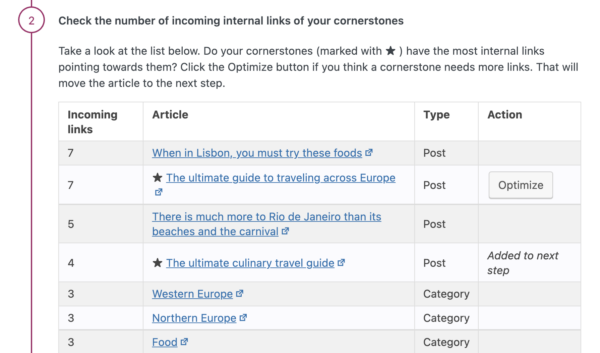
Yoast SEO’s text link counter visualizes your links so you can optimize them. It shows the internal links in a post and the internal links to a post. This tool can enhance your site structure by improving the links between your related posts. Make sure your cornerstones get the most (relevant) links! You can identify your cornerstones by finding them in the column with the pyramid icon.

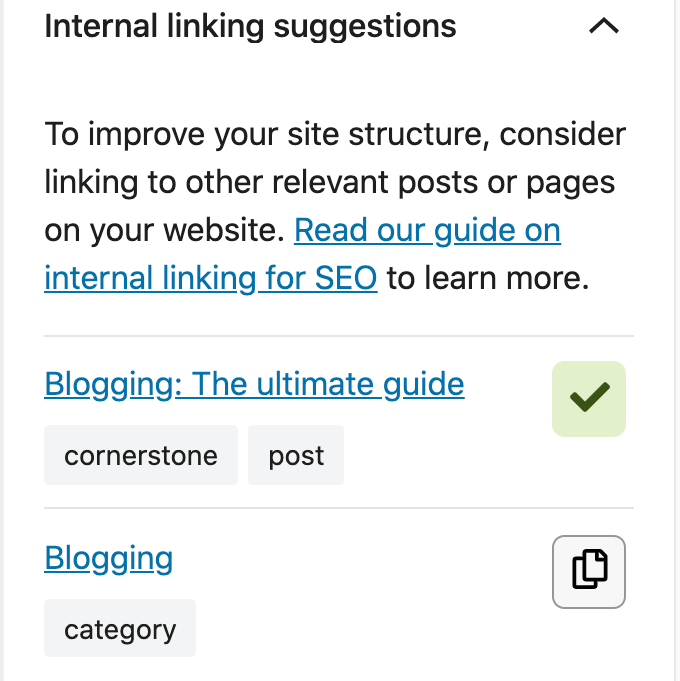
Yoast SEO Premium helps you with your internal linking as well. Our internal linking suggestions tool will show you which articles are related to the one you’re writing, so you can easily link to them: just by dragging the link into your editor!
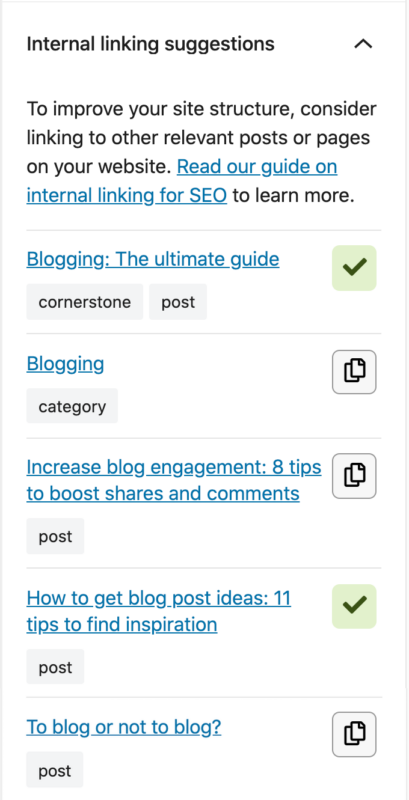
Moreover, our tool allows you to indicate which articles you consider cornerstone content on your site. Those articles will be shown at the top of the internal linking suggestions. You’ll never forget to link to them again.
Read on: How to use Yoast SEO for your cornerstone content strategy »
The importance of site structure
As we have seen, there are several reasons why site structure is important. A good site structure helps both your visitors and Google navigate your site. It makes it easier to implement changes and prevents competing with your content. So use the tips and pointers in this guide to check and improve your site structure. That way, you’ll stay on top and keep your website from growing out of control!
Want to improve your site structure but don’t know where to start? Get Yoast SEO Premium and get loads of helpful tools and guidance, including free access to Yoast SEO Academy, our Site structure training, and our SEO workouts!
Keep on reading: WordPress SEO: The definitive guide to higher rankings for WordPress sites »
Marieke van de Rakt
Marieke was head of strategy and former CEO at Yoast. After the sale of Yoast to Newfold Digital in 2021 she is no longer active at Yoast in 2023. Marieke, together with her husband Joost, actively invests in and advises several startups through their company Emilia Capital.
Source :
https://yoast.com/site-structure-the-ultimate-guide/