QuTS hero h5.1.0
2023-05-29
QuTS hero h5.1.0 brings many important new features to further enhance security, improve performance, and boost productivity for your QNAP NAS. You can now log in with more secure verification methods, delegate administrative tasks to general users, and centrally manage NAS devices via AMIZ Cloud. You can also benefit from smarter disk migration, smoother file browsing and search in File Station, more powerful SMB signing and file sharing, more convenient storage pool expansion, and much more. See What’s New to learn about main features and Other Changes to learn about other features, enhancements, and changes.
We also include fixes for reported issues and provide information about known issues. For details, see Fixed and Known Issues. You should also see Important Notes before updating QuTS hero.
What’s New
- Storage pool expansion by adding disks to an existing RAID group
- Support for SMB multichannel
- AES-128-GMAC algorithm support for SMB signing
- Delegated Administration for better organization flexibility and productivity
- 2-step verification and passwordless login for enhanced account security
- Centralized NAS management with AMIZ Cloud
- Automatic disk replacement with Predictive Migration before potential failure
- Lists of recent files in File Station for easier file browsing
- File content search in File Station with Qsirch integration
Storage pool expansion by adding disks to an existing RAID group
Users can now expand a storage pool by adding disks to expand an existing RAID group within the pool. When expanding the RAID group, users can also migrate the RAID group to a different RAID type.
To use this function, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots, select a storage pool, click Manage > Storage Pool > Action > Expand Pool to open the Expand Storage Pool Wizard, and then select Add new disk(s) to an existing RAID group.

Support for SMB multichannel
Users can now allow SMB 3.x clients to establish multiple network connections simultaneously to an SMB file share. Multichannel can increase the network performance by aggregating network bandwidth over multiple NICs and mitigating network disruption by increasing network fault tolerance.
To enable SMB multichannel, go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Win/Mac/NFS/WebDAV > Microsoft Networking, and then select Enable SMB Multichannel.
SMB multichannel is only supported on the following clients using SMB 3.0 or later:
- Windows 8.1 and later
- Windows Server 2012 and later
- macOS Big Sur 11.3.1 and later

AES-128-GMAC algorithm support for SMB signing
QuTS hero h5.1.0 now supports the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Galois Message Authentication Code (GMAC) cipher suite for SMB signing. SMB signing can use this algorithm to encode and decode using 128-bit keys and can automatically negotiate this method when connecting to a client device that also supports the same algorithm standard.
To enable SMB signing, go to Control Panel > Network & File Services > Win/Mac/NFS/WebDAV > Microsoft Networking > Advanced Settings, and then configure the SMB signing settings. Make sure that you select the highest SMB version as SMB 3.

Delegated Administration for better organization flexibility and productivity
In modern organizations, IT administrators are often overwhelmed by a sheer number of tasks and responsibilities. QuTS hero h5.1.0 now supports Delegated Administration, which allows administrators to delegate various roles to general users, so that they can perform routine tasks, control their data, manage system resources, and monitor device status even when IT administrators are not available. You can choose from a wide range of roles, including System Management, Application Management, Backup Management, Shared Folder Management, and many more. To ensure system security, we recommend only granting permissions that are essential for performing required tasks.
This feature not only helps reduce the workloads of administrators but also greatly enhances productivity and flexibility for your organization. You can also easily view the roles currently assigned to each user and change their roles anytime according to your needs. To configure these settings, go to Control Panel > Privilege > Delegated Administration. To learn more about Delegated Administration, check QuTS hero h5.1.0 User Guide.

2-step verification and passwordless login for enhanced account security
QuTS hero now supports passwordless login, which replaces your password with a more secure verification method. Instead of entering a password, you can scan a QR code or approve a login request with your mobile device to verify your identify. QuTS hero now also supports more verification methods for 2-step verification. In addition to a security code (TOTP), you can also choose to scan a QR code, approve a login request, or enter an online verification code to add an extra layer of security to protect your NAS account.
To configure these settings, go to the NAS desktop, click your username on the taskbar, and then select Login and Security. You can download and install QNAP Authenticator from App Store or Google Play and pair this mobile app with your NAS to secure your NAS account. Note that you cannot use 2-step verification and passwordless login at the same time.

Centralized NAS management with AMIZ Cloud
You can now add the NAS to an organization when setting up the myQNAPcloud service for your NAS. This allows organization administrators to remotely access, manage, and monitor various system resources on the NAS via AMIZ Cloud, a central cloud management platform designed for QNAP devices.
To manage the NAS via AMIZ Cloud, you must enable AMIZ Cloud Agent in myQNAPcloud. This utility communicates with AMIZ Cloud and collects the data of various resources on your device for analytics purposes without any identifiable person information.

Automatic disk replacement with Predictive Migration before potential failure
Predictive Migration is a major improvement over the original Predictive S.M.A.R.T. Migration feature in Storage & Snapshots. This upgrade now allows users to specify multiple trigger events that prompt the system to automatically replace a disk before it fails.
Besides S.M.A.R.T. warnings, users can also specify trigger events from other monitoring systems such as Western Digital Device Analytics (WDDA), IronWolf Health Management (IHM), DA Drive Analyzer, and SSD estimated remaining life. When a specified trigger event occurs—for example, a disk ‘s Galois WDDA status changes to “Warning” or the SSD estimated remaining life reaches 3%—the system automatically replaces the disk and migrates all its data to a spare disk. This process protects your data better and is safer than manually initiating a full RAID rebuild after the disk fails.
To configure Predictive Migration, go to Storage & Snapshots > Global Settings > Disk Health.
Lists of recent files in File Station for easier file browsing
With the new Recent Files feature in File Station, you can now easily locate files that were recently uploaded, opened, or deleted. These three folders are conveniently grouped together under the Recent File folder at the upper left portion of File Station.

File content search in File Station with Qsirch integration
The original search function in File Station could only search for file names of a specific file type. With the integration of Qsirch into File Station, you can now search for file content using keywords, and also search for multiple file types using these keywords at the same time. To use this feature, you need to install Qsirch, an app that can index the files on your device and greatly facilitate your file search.

Other Changes
Control Panel
- Users can now configure an individual folder to inherit permissions from its parent folder or to remove the inherited permissions anytime. Users can also make a folder extend its permissions to all its subfolders and files. To configure permission inheritance on a folder, go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders, and then click the Edit Shared Folder Permissions icon under Action.
- Added additional specification information for memory slots in Control Panel > System Status > Hardware Information.
- Changed the behavior and the description of certain permission settings as we do not recommend using the default administrator account “admin”.
- Optimized the process of restoring the LDAP database.
- The “Network Recycle Bin” feature has been renamed to “Recycle Bin” in Network & File Services.
- The automatic firmware update settings have been streamlined with the following changes: – The selectable options for automatic firmware updates have been greatly simplified. Users now select one of three firmware types to automatically update their system with: quality updates, critical updates, or latest updates. – “Security updates” are now “critical updates”. Critical updates include security fixes as well as critical system issue fixes. – “Quality updates” now include security fixes and critical issue fixes in addition to bug fixes.- “Feature updates” are now “latest updates” and include quality and critical updates in addition to new features, enhancements, and bug fixes. – Update notifications no longer need to be enabled separately for each firmware type. Notifications are now either enabled or disabled for all firmware types.
- The time interval for observing successive failed login attempts can now be configured to be between 0 and 600 minutes. Moreover, a time interval of 0 minutes means that failed login attempts are never reset.
- You can now include more information from account profiles when importing and exporting user accounts.
- You can now select the direction to append the custom header for the reverse proxy rule.
- Users can now edit and enable or disable existing power schedules in Control Panel > System > Power > Power Schedule. Previously, users could only add or remove power schedules.
- The “Network Recycle Bin” feature has been renamed to “Recycle Bin” in Network & File Services.
Desktop & Login
- You can now log out of your account on all devices, browsers, and applications at once. To use this feature, go to the desktop, click your username on the taskbar, and then go to Login and Security > Password.
- Added an icon on the top-right corner of the desktop to indicate whether the device has enabled myQNAPcloud and been associated with a QNAP ID or whether the device has joined AMIZ Cloud.
- Users can now save their QuTS Hero login credentials in their web browser. To enhance the security of your QuTS Hero user account, we recommend enabling 2-step verification.
App Center
- Users can now configure a schedule for automatic installations of app updates.
File Station
- Added prompt banners to remind users to turn on related browsing functions for multimedia files.
- Enhanced the Background Tasks display UI.
- Improved File Station performance and enhanced file browsing experience.
Help Center
- Redesigned the user interface of Help Center for a better user experience.
Initialization
- You can now purchase licenses during QuTScloud installation.
iSCSI & Fibre Channel
- Added a new settings page for managing default iSCSI CHAP authentication settings, which you can use for multiple iSCSI targets. You can find these settings in iSCSI & Fibre Channel > Global Settings > Default iSCSI CHAP. When creating or editing a target, you can choose to use the default CHAP settings or configure unique settings for the target.
- Added the client umask feature to assign default permissions for existing and new files and folders.
- When creating an iSCSI target, you can now select the network interfaces that an iSCSI target will use for data transmission. Previously, users could only do so after the target was created.
Network & Virtual Switch
- Network & Virtual Switch can now record event logs when the system identifies conflicting IP addresses between the local device and another device on the same network.
- Users can now configure the MAC address when creating or modifying a virtual switch.
- When selecting the system default gateway automatically, you can now configure the checking target by specifying the domain name or IP address.
NFS
- NFS service now supports both NFSv4 and NFSv4.1 protocols.
- Users can now set the rcpbind to assign fixed ports to RPC services. Make sure that you configure the firewall rules accordingly to allow connections only on the fixed ports.
PHP System Module
- Updated the built-in PHP version to 8.2.0.
Resource Monitor
- Resource Monitor now displays the space used by files created from Qsync file versioning.
SAMBA
- Updated Samba to version 4.15.
- You can now aggregate up to 50 shared folders on a Windows network.
Storage & Snapshots
- Added support for disk failure prediction from ULINK’s DA Drive Analyzer. Registered users of DA Drive Analyzer can now also monitor disk failure prediction statuses in Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD > Disks.
- Added support for Seagate dual-actuator disks. These disks appear with a “Seagate DA” tag in Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD > Disks.
- Added support for Western Digital Device Analytics (WDDA) for Western Digital (WD) disks. To view WDDA information, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD > Disks, select a WD disk, and click Health > View Details.
- Improved the “Enable Read Acceleration” feature so that it not only improves the read performance of new files added to a shared folder (starting in QuTS hero h5.0.1), but also improves the read performance of existing files (starting in QuTS hero h5.1.0). This feature can be enabled for shared folders after upgrading from QuTS hero h5.0.0 or earlier to QuTS hero h5.0.1 or later.
- Increased the maximum number of disks in RAID-TP from 16 to 24.
- Redesigned the presentation of disk information into tabular format for enhanced user experience, now viewable in Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD > Disks.
- Renamed the function “Replace & Detach” to “Replace” and added the option for users to choose whether to designate the replaced disk as a spare disk or to detach it from the system.
- You can now select up to 24 disks for a single RAID-TP group.
- Encrypted LUNs are now supported in VJBOD, SnapSync, Snapshot Replica, and snapshot import/export operations.
- Improved the user interface on various snapshot-related screens.
- Users can now change the destination IP address in Snapshot Replica jobs.
- Added a new window that automatically appears when you insert new disks and helps you decide what to do with them. You can also access this window any time by going to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD > Disks > More > Manage Free Disks.
- After rebuilding a RAID group with a spare disk, the failed disk’s slot becomes reserved for a spare disk. To free up this slot for other purposes, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Disks/VJBOD > Disks, select the disk slot, and click Action > Free Up Spare Disk Slot.
- Users can now enable and disable QNAP SSD Antiwear Leveling (QSAL) on an existing SSD storage pool any time. Richer information is also available for QSAL-enabled pools, including replacement priority recommendation and charts showing the remaining capacity and life of the SSDs in the pool. To configure QSAL or view QSAL information, go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots, click an SSD storage pool, and then click Manage > QSAL.
System
- You now need to enter a verification code when resetting your password if you forgot your password. This extra step helps enhance your account security.
Important Note
- In QuTS Hero h5.0.1 or earlier, users can no longer create new VJBOD disks from a remote NAS if the remote NAS is running QuTS Hero h5.1.0 or later. If there are existing VJBOD disks connections to the remote NAS before it is updated to QuTS Hero h5.1.0 or later, these VJBOD disks are unaffected and remain operational after the update. In QuTS Hero h5.1.0 or later, users can still create VJBOD disks from a remote NAS running QuTS Hero h5.0.1 or earlier.
- Removed support for CO Video.
Source :
https://www.qnap.com/en/release-notes/quts_hero/overview/h5.1.0











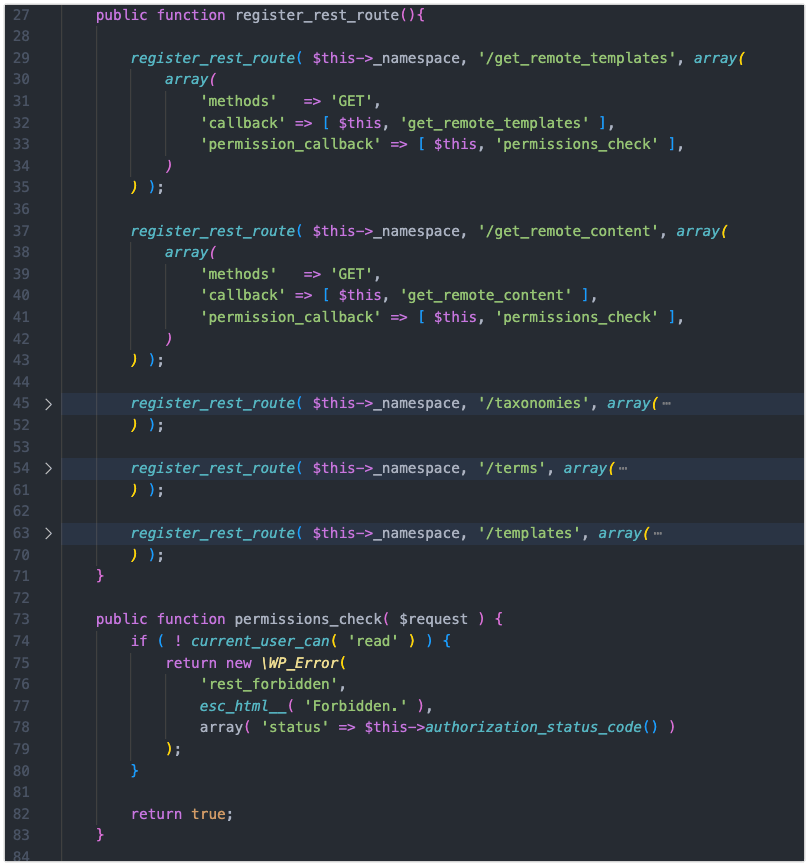
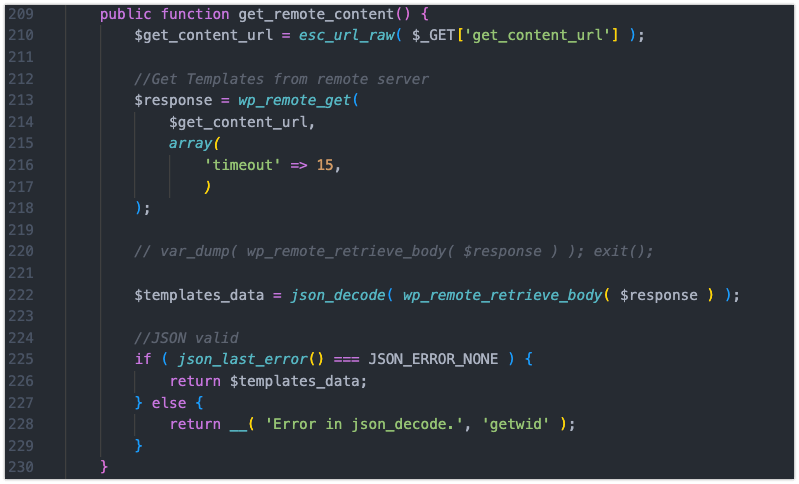











 Fun fact: In my environment that change made the deletions go 30 times faster!!!
Fun fact: In my environment that change made the deletions go 30 times faster!!!