DNS tunneling is a technique that encodes data of other programs and protocols in DNS queries, including data payloads that can be used to control a remote server and applications. Because of this, DNS tunneling – and DNS exfiltration associated with it by threat actors – is of great concern to many IT and SecOps teams. Fortunately, new developments in the Cisco Umbrella DNS cache system allow for faster and more reliable detection of DNS tunneling and exfiltration events.
How Does DNS Tunneling Work?
DNS tunneling revolves around the transfer of data. So, if we have:
- Input Data data – Name: Alice, Age: 25, SSN: 123-45-678
Using DNS exfiltration, we can encode and send this data placed in several subdomains of the domain under our control as a single entry:
- jzqw2zj2ifwg.sy3ffrawozj2.gi2syu2tjy5d.cmrtfu2djljw.my.tunnel.com
Or, we can use multiple entries using multiple queries to large numbers of domains:
- jzqw2.zj2if.my.tunnel.com
- wgsy3.ffraw.my.tunnel.com
- ozj2g.i2syu.my.tunnel.com
- 2tjy5.dcmrt.my.tunnel.com
Users can abuse this technique – as seen in Fig. 1 below – by installing a free DNS tunneling tool to bypass IT policies and/or monitoring. They can also use this technique to bypass network authorization to obtain free internet access in hotels and airports.

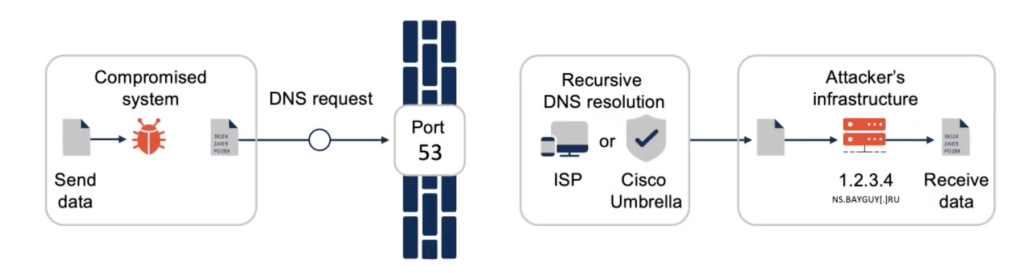
Attackers can use outbound DNS requests to send encoded exfiltrated data to their infrastructure – as seen in Fig. 2 below – or use DNS responses to send commands to compromised systems and manage infected devices remotely.
Improvements to DNS Tunneling Realtime Detection
Today, we’re thrilled to announce that organizations have a powerful new ally to protect against data exfiltration and unauthorized DNS tunnels in their networks. Cisco Umbrella has developed a new proprietary cache within our DNS resolvers to work alongside our machine learning modules. Our newest machine learning module is tuned to detect data exfiltration and DNS tunneling events.
This new module monitors DNS traffic for behavioral patterns and traffic exfiltrating data, efficiently building enough information to detect and block data exfiltration. And, in the event circumstances and domain reputations change, this module will correct itself and let traffic through.
We made this update because, over the past couple of years, we’ve seen organizations more productive and more connected amidst the new reality of working digitally during the pandemic. The explosion of logins and bandwidth, though, has at times come with reductions in digital security. Data exfiltration has become a new reality, and one hole attackers punch is in the DNS.
Powering Improvements With a Revolutionary DNS Cache
The technology stack powering Cisco Umbrella’s DNS resolvers handles blistering loads of DNS traffic from ISPs, global organizations, municipalities, schools, and homes. Building on this, we’ve hacked the heart of the DNS resolver – the cache. And while we dig into the details of this new functionality in our DNS tunneling solution brief, we also want to provide you with an overview here.
The cache of a DNS resolver enables serving the swell of global traffic without fault, outage, and ease. It also insulates the backbone of the internet from being overwhelmed with identical queries. Caches store data locally so that it can be served quicker.
Tunneling Cache

The tunneling cache enables us to glue together a sequence of queries that are otherwise distinct atomic events. With proprietary key and data fields, we seamlessly incorporate rapid cache updates unbeknownst to web surfers. We maintain lightning speed throughout by merging incoming data fields using tricks found in probabilistic algorithms. Gluing together each individual’s DNS queries provides access to a rich amount of information, otherwise hidden. Organizations can now get personalized DNS tunneling monitoring, detection, and enforcement in real time.
Encryption Payloads

We pair the new DNS cache with a lexical engine highly trained at identifying encrypted messages. Our researchers dug into various encryption protocols and created a stateful algorithm capable of churning through every character transition in a domain name and identifying encryption payloads with high fidelity.
Take DNS-Layer Security to the Next Level
Cisco Umbrella analyzes internet activity to uncover known and emergent threats in order to protect users anywhere they go. Together, these capabilities power Umbrella to predict and prevent DNS tunneling attacks before they happen. Enabling this security category reduces the risk of DNS tunneling and potential data loss. Organizations can choose to block users from using DNS tunneling VPN services, or they can monitor the results in reports, providing flexibility to determine what is suitable given their risk tolerance.
Address your DNS blind spot by enforcing security over port 53 both on and off the corporate network. Request a personalized demo of Cisco Umbrella today to explore how this exciting new feature can help protect your enterprise.
Source :
https://umbrella.cisco.com/blog/improvements-dns-tunneling-dns-exfiltration-detection