By: Mayumi Nishimura
October 06, 2023
Read time: 4 min (1096 words)
Digitalization has changed the business environment of the electric power industry, exposing it to various threats. This webinar will help you uncover previously unnoticed threats and develop countermeasures and solutions.
The Electric utility industry is constantly exposed to various threats, including physical threats and sophisticated national-level cyber attacks. It has been an industry that has focused on security measures. But in the last few years, power system changes have occurred. As OT becomes more networked and connected to IT, the number of interfaces between IT and OT increases, and various cyber threats that have not surfaced until now have emerged.
Trend Micro held a webinar to discuss these changes in the situation, what strategies to protect your company’s assets from the latest cyber threats, and the challenges and solutions in implementing these strategies.
This blog will provide highlights from the webinar and share common challenges in the power industry that emerged from the survey. We hope that this will be helpful to cybersecurity directors in the Electric utility industry who recognize the need for consistent security measures for IT and OT but are faced with challenges in implementing them.
Click here to watch the On-demand Webinar
Vulnerabilities in Electric Power Systems
In the webinar, we introduced examples of threats from “Critical Infrastructures Exposed and at Risk: Energy and Water Industries” conducted by Trend Micro. The main objective of this study was to demonstrate how easy it is to discover and exploit OT assets in the water and energy sector using basic open-source intelligence (OSINT) techniques. As a result of the investigation, it was possible to access the HMI remotely, view the database containing customer data, and control the start and stop of the turbine.
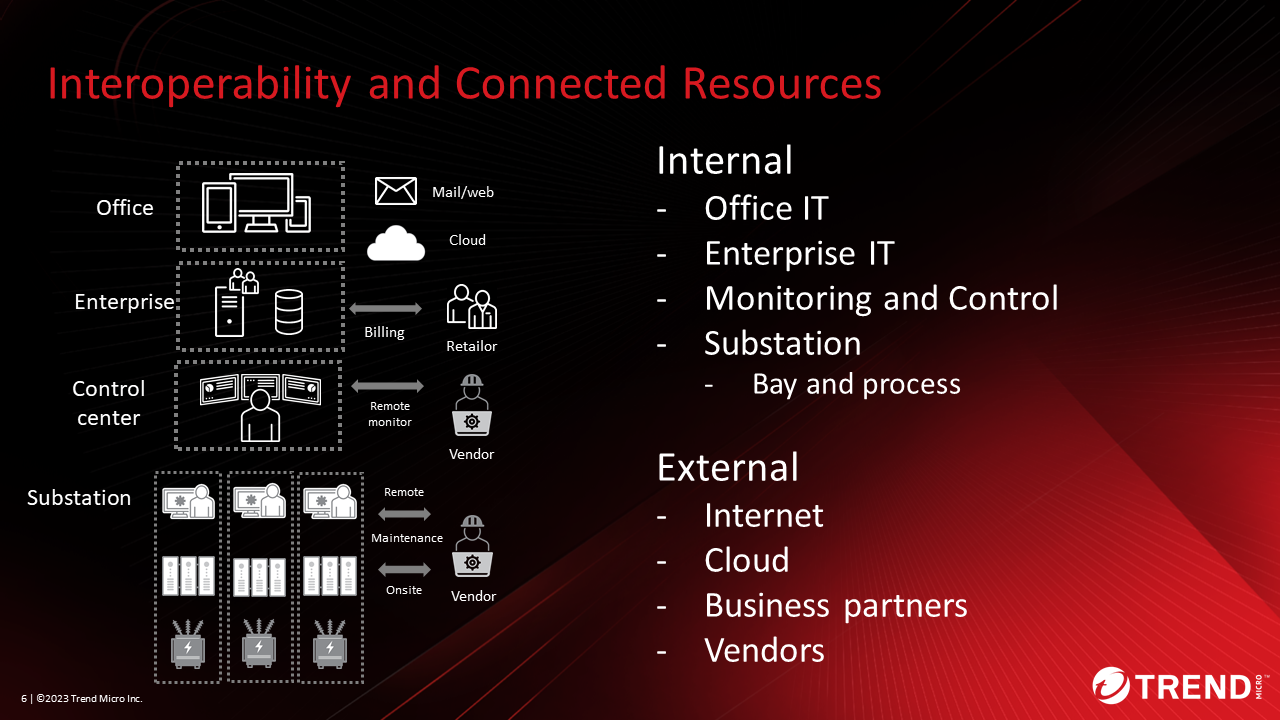
Cyberattacks Against Electric Power
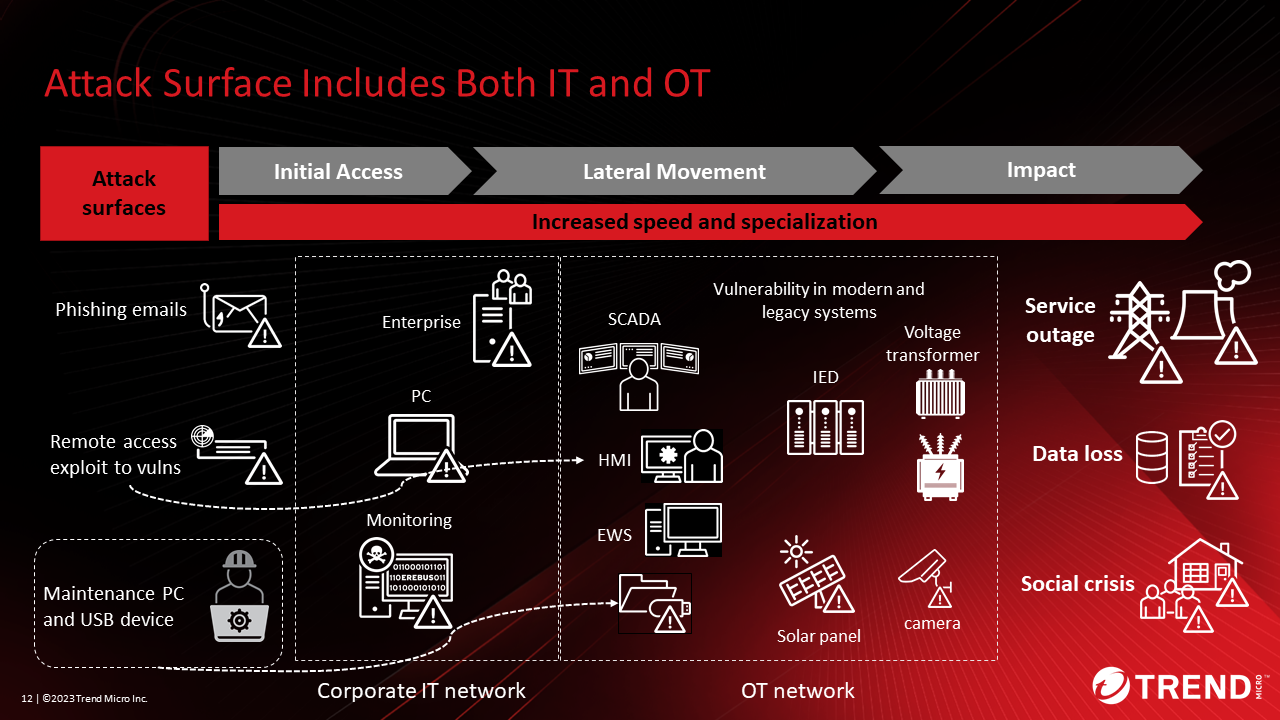
Explained the current cyberattacks on electric power companies. Figure 2 shows the attack surface (attack x digital assets), attack flow, and ultimately, possible damage in IT and OT of energy systems.
An example of an attack surface in an IT network is an office PC that exploits VPN vulnerabilities. If attackers infiltrate the monitoring system through a VPN, they can seize privileges and gain unauthorized access to OT assets such as the HMI. There is also the possibility of ransomware being installed.
A typical attack surface in an OT network is a PC for maintenance. If this terminal is infected with a virus and a maintenance person connects to the OT network, the virus may infect the OT network and cause problems such as stopping the operation of the OT equipment.
To protect these interconnected systems, it is necessary to review cybersecurity strategies across IT, OT, and different technology domains.
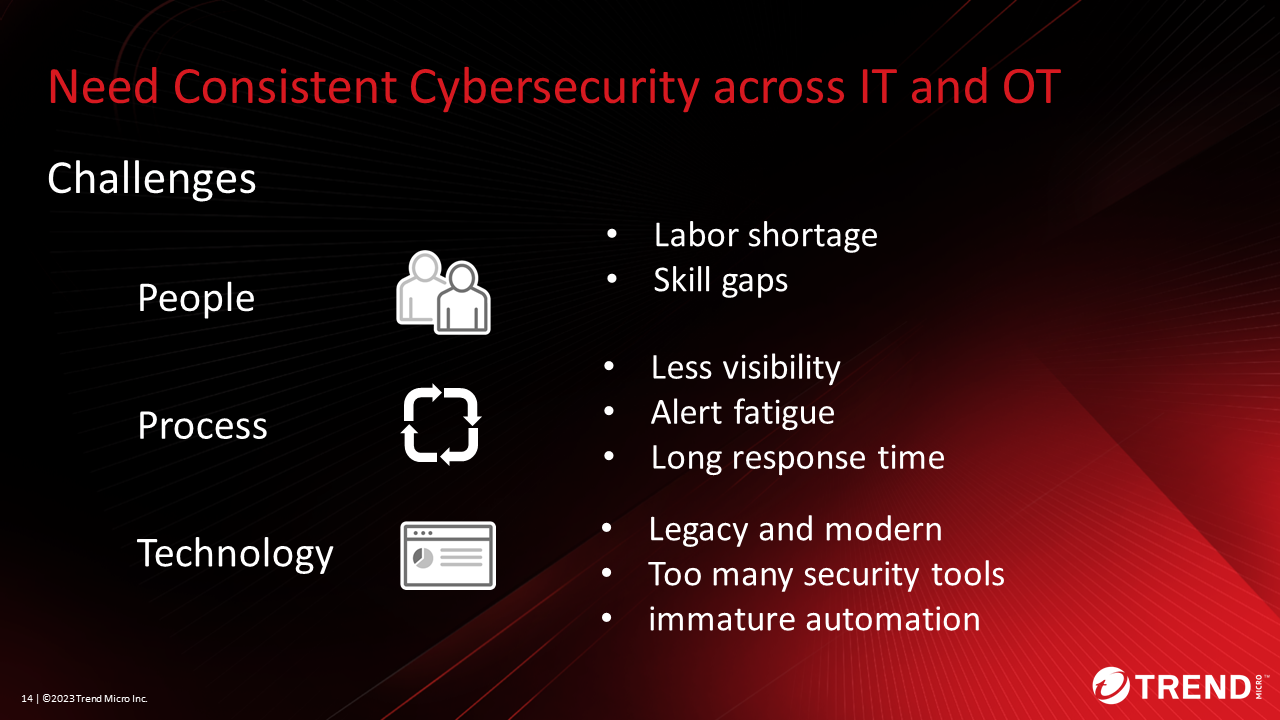
Solutions
We have organized the issues from People, Process, and Technology perspectives when reviewing security strategies across different technology domains such as IT and OT.
One example of people-related issues is labor shortages and skills gaps. The reason for the lack of skills is that IT security personnel are not familiar with the operations side, and vice versa. In the webinar, we introduced three ideas for approaches to solving these people’s problems.
The first is improving employee security awareness and training. From management to employees, we must recognize the need for security and work together. Second, to understand the work of the IT and OT departments, we recommend job rotation and workshops for mutual understanding. The third is documentation and automation of incident response. Be careful not to aim for automation. First, it is important to identify unnecessary tasks and reduce work. After that, we recommend automating the necessary tasks. We also provide examples of solutions for Process and Technology issues in the webinar.
Finally, we introduced Unified Kill Chain as an effective approach. It extends and combines existing models such as Lockheed Martin’s Cyber KillChain® and MITER’s ATT&CK™ to show an attacker’s steps from initiation to completion of a cyber attack. The attacker will not be able to reach their goal unless all of these steps are completed successfully, but the defender will need to break this chain at some point, which will serve as a reference for the defender’s strategy. Even when attacks cross IT and OT, it is possible to use this approach as a reference to evaluate the expected attacks and the current security situation and take appropriate security measures in response.

The Webinar’s notes
To understand the situation and thoughts of security leaders in the Electric utility industry, we have included some of the survey results regarding this webinar. The webinar, held on June 29th, was attended in real time by nearly 100 people working in the energy sector and engaged in cybersecurity-related work.
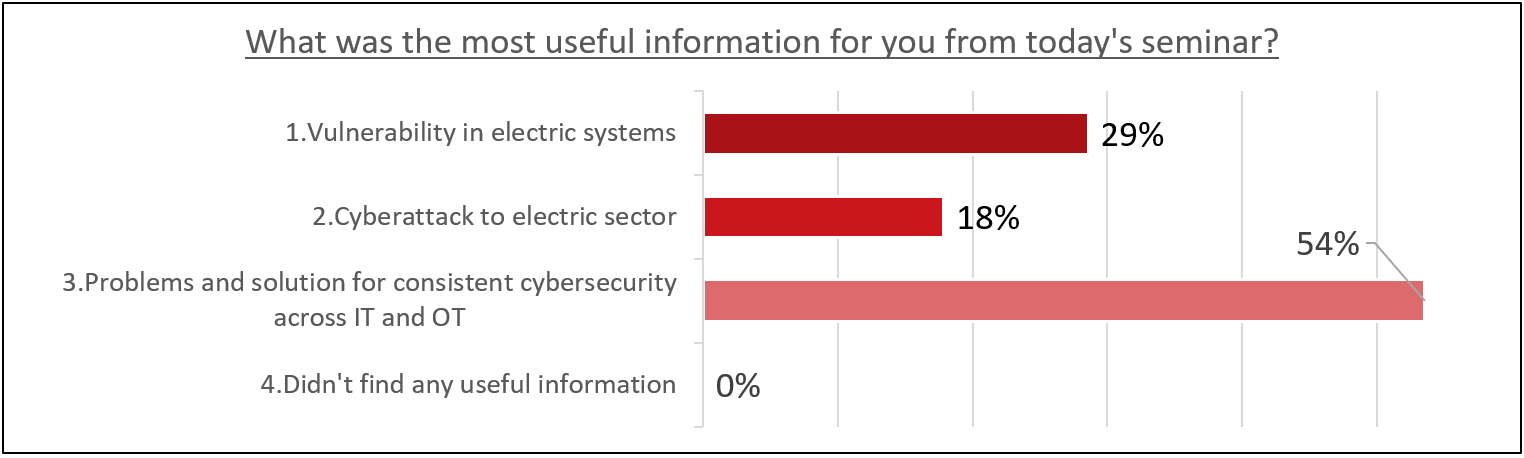
When asked what information they found most helpful, the majority of survey respondents selected “consistent cybersecurity issues and solutions across IT and OT,” indicating that “consistent cybersecurity issues and solutions across IT and OT.” I am glad that I was able to help those who feel that there are issues in implementing countermeasures.
Also, over 90% of respondents answered “Agree” when asked if they needed consistent cybersecurity across IT and OT. Among those who chose “Agree”, 39% answered that they have already started some kind of action, indicating the consistent importance of cybersecurity in IT and OT.
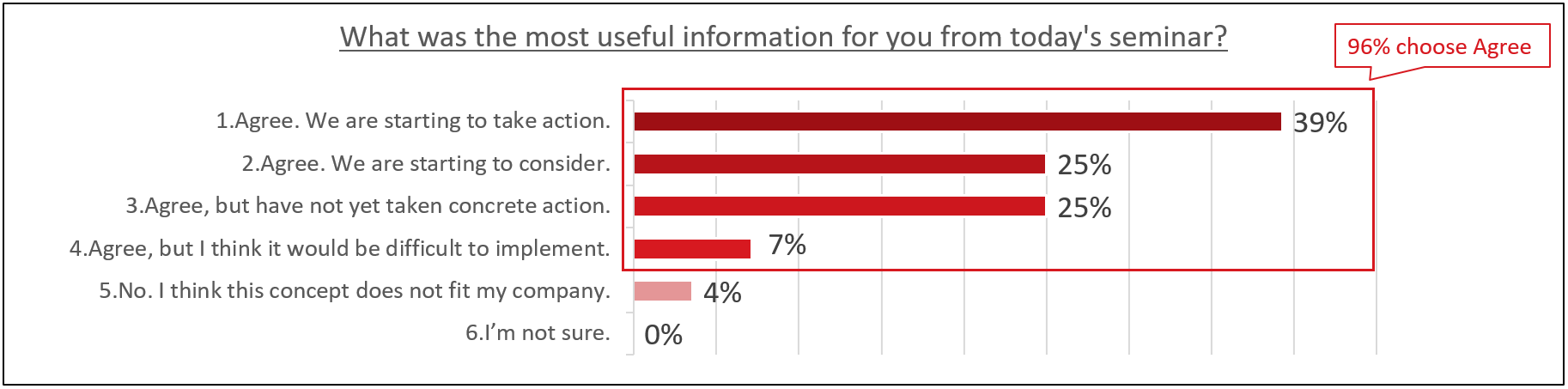
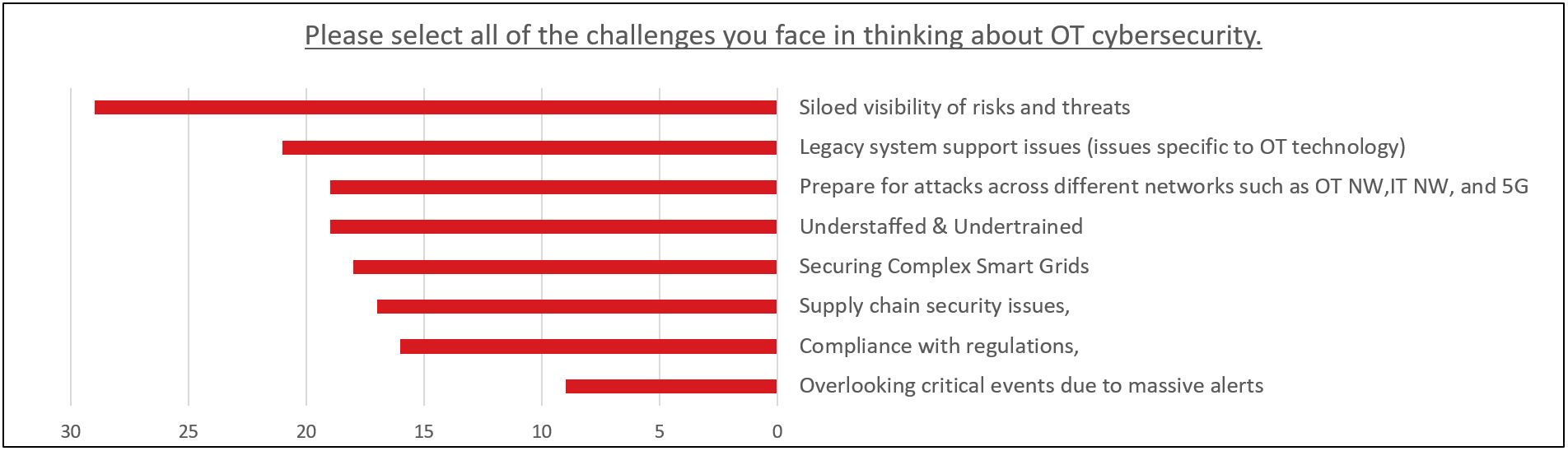
Lastly, I would like to share the results of a question asked during webinar registration about what issues people in this industry think about OT security. Number one was siloed risk and threat visibility, and number two was legacy system support. The tie for 3rd place was due to a lack of preparation for attacks across different NWs and lack of staff personnel/skills. There is a strong sense of challenges in the visualization of risks and threats, other organizational efforts, and technical countermeasures.
Resources
The above is a small excerpt from the webinar. We recommend watching the full webinar video below if you are interested in the power industry’s future cybersecurity strategy.
Click here to watch the On-demand Webinar
In addition, Trend Micro reports introduced in the webinar and other reference links related to the energy industry can be accessed below.
Tech Paper
ICS/OT Security for the Electric Utility
Critical Infrastructures Exposed and at Risk: Energy and Water Industries
VIDEO
Electric utilities need to know cross domain attack
Blog
Electricity/Energy Cybersecurity: Trends & Survey Response