These statistics are based on detection verdicts of Kaspersky products and services received from users who consented to providing statistical data.
Quarterly figures
According to Kaspersky Security Network, in Q2 2022:
- Kaspersky solutions blocked 1,164,544,060 attacks from online resources across the globe.
- Web Anti-Virus recognized 273,033,368 unique URLs as malicious. Attempts to run malware for stealing money from online bank accounts were stopped on the computers of 100,829 unique users.
- Ransomware attacks were defeated on the computers of 74,377 unique users.
- Our File Anti-Virus detected 55,314,176 unique malicious and potentially unwanted objects.
Financial threats
Financial threat statistics
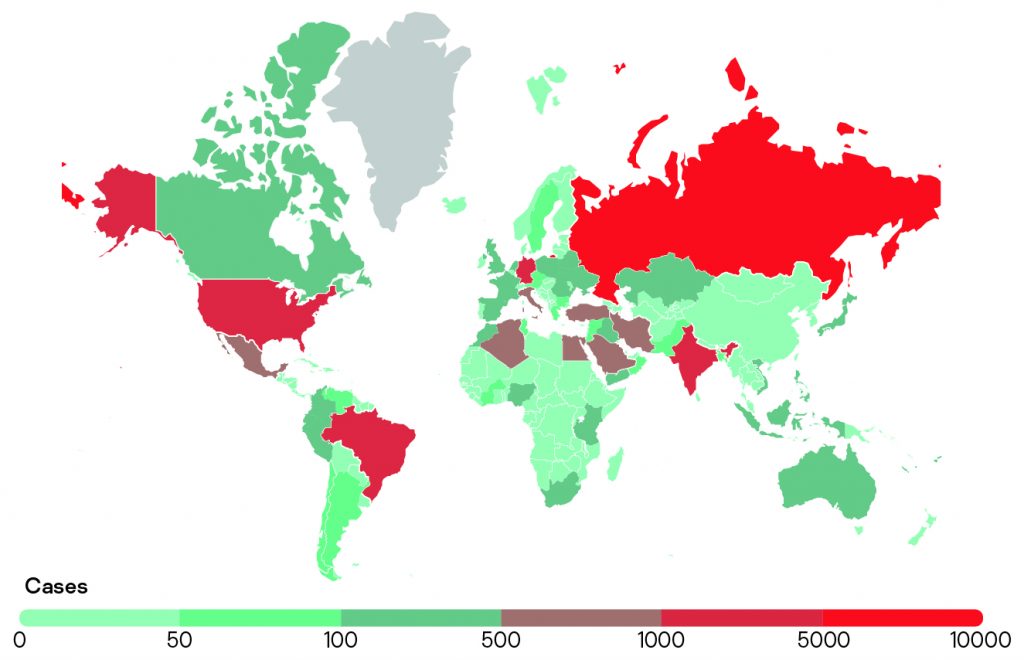
In Q2 2022, Kaspersky solutions blocked the launch of malware designed to steal money from bank accounts on the computers of 100,829 unique users.
https://e.infogram.com/_/xVIqEwzQRE40afesiEuD?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Number of unique users attacked by financial malware, Q2 2022 (download)
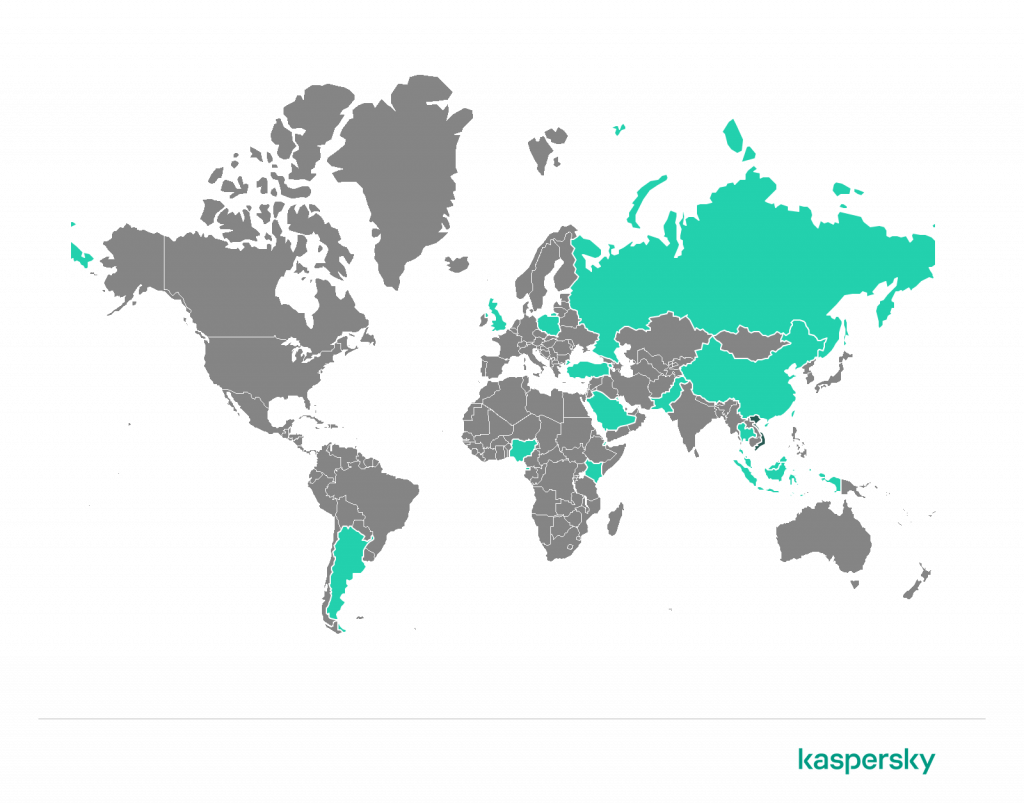
Geography of financial malware attacks
To evaluate and compare the risk of being infected by banking Trojans and ATM/POS malware worldwide, for each country and territory we calculated the share of Kaspersky users who faced this threat during the reporting period as a percentage of all users of our products in that country or territory.
https://e.infogram.com/_/VAlc8RYhTGIEk24LI7Q3?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Geography of financial malware attacks, Q2 2022 (download)
TOP 10 countries and territories by share of attacked users
| Country or territory* | %** | |
| 1 | Turkmenistan | 4.8 |
| 2 | Afghanistan | 4.3 |
| 3 | Tajikistan | 3.8 |
| 4 | Paraguay | 3.1 |
| 5 | China | 2.4 |
| 6 | Yemen | 2.4 |
| 7 | Uzbekistan | 2.2 |
| 8 | Sudan | 2.1 |
| 9 | Egypt | 2.0 |
| 10 | Mauritania | 1.9 |
* Excluded are countries and territories with relatively few Kaspersky product users (under 10,000).
** Unique users whose computers were targeted by financial malware as a percentage of all unique users of Kaspersky products in the country.
TOP 10 banking malware families
| Name | Verdicts | %* | |
| 1 | Ramnit/Nimnul | Trojan-Banker.Win32.Ramnit | 35.5 |
| 2 | Zbot/Zeus | Trojan-Banker.Win32.Zbot | 15.8 |
| 3 | CliptoShuffler | Trojan-Banker.Win32.CliptoShuffler | 6.4 |
| 4 | Trickster/Trickbot | Trojan-Banker.Win32.Trickster | 6 |
| 5 | RTM | Trojan-Banker.Win32.RTM | 2.7 |
| 6 | SpyEye | Trojan-Spy.Win32.SpyEye | 2.3 |
| 7 | IcedID | Trojan-Banker.Win32.IcedID | 2.1 |
| 8 | Danabot | Trojan-Banker.Win32.Danabot | 1.9 |
| 9 | BitStealer | Trojan-Banker.Win32.BitStealer | 1.8 |
| 10 | Gozi | Trojan-Banker.Win32.Gozi | 1.3 |
* Unique users who encountered this malware family as a percentage of all users attacked by financial malware.
Ransomware programs
Quarterly trends and highlights
In the second quarter, the Lockbit group launched a bug bounty program. The cybercriminals are promising $1,000 to $1,000,000 for doxing of senior officials, reporting web service, Tox messenger or ransomware Trojan algorithm vulnerabilities, as well as for ideas on improving the Lockbit website and Trojan. This was the first-ever case of ransomware groups doing a (self-promotion?) campaign like that.
Another well-known group, Conti, said it was shutting down operations. The announcement followed a high-profile attack on Costa Rica’s information systems, which prompted the government to declare a state of emergency. The Conti infrastructure was shut down in late June, but some in the infosec community believe that Conti members are either just rebranding or have split up and joined other ransomware teams, including Hive, AvosLocker and BlackCat.
While some ransomware groups are drifting into oblivion, others seem to be making a comeback. REvil’s website went back online in April, and researchers discovered a newly built specimen of their Trojan. This might have been a test build, as the sample did not encrypt any files, but these events may herald the impending return of REvil.
Kaspersky researchers found a way to recover files encrypted by the Yanluowang ransomware and released a decryptor for all victims. Yanluowang has been spotted in targeted attacks against large businesses in the US, Brazil, Turkey, and other countries.
Number of new modifications
In Q2 2022, we detected 15 new ransomware families and 2355 new modifications of this malware type.
https://e.infogram.com/_/LLQNUsWe0kQuAyykdQ9p?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Number of new ransomware modifications, Q2 2021 — Q2 2022 (download)
Number of users attacked by ransomware Trojans
In Q2 2022, Kaspersky products and technologies protected 74,377 users from ransomware attacks.
https://e.infogram.com/_/YAmZLBPilFKmsbsxFKpJ?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Number of unique users attacked by ransomware Trojans, Q2 2022 (download)
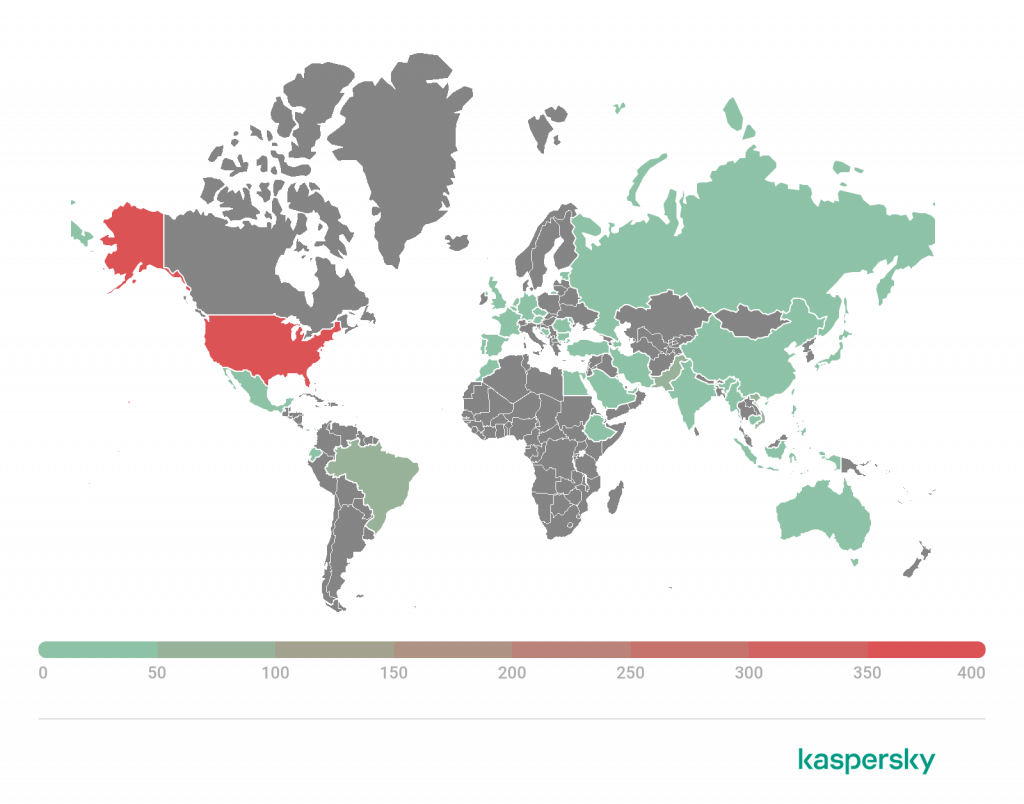
Geography of attacked users
https://e.infogram.com/_/oDrJKQvRPnVf4zT5I0kp?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Geography of attacks by ransomware Trojans, Q2 2022 (download)
TOP 10 countries and territories attacked by ransomware Trojans
| Country or territory* | %** | |
| 1 | Bangladesh | 1.81 |
| 2 | Yemen | 1.24 |
| 3 | South Korea | 1.11 |
| 4 | Mozambique | 0.82 |
| 5 | Taiwan | 0.70 |
| 6 | China | 0.46 |
| 7 | Pakistan | 0.40 |
| 8 | Angola | 0.37 |
| 9 | Venezuela | 0.33 |
| 10 | Egypt | 0.32 |
* Excluded are countries and territories with relatively few Kaspersky users (under 50,000).
** Unique users whose computers were attacked by Trojan encryptors as a percentage of all unique users of Kaspersky products in the country.
TOP 10 most common families of ransomware Trojans
| Name | Verdicts* | Percentage of attacked users** | |
| 1 | Stop/Djvu | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Stop | 17.91 |
| 2 | WannaCry | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Wanna | 12.58 |
| 3 | Magniber | Trojan-Ransom.Win64.Magni | 9.80 |
| 4 | (generic verdict) | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Gen | 7.91 |
| 5 | (generic verdict) | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Phny | 6.75 |
| 6 | (generic verdict) | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Encoder | 6.55 |
| 7 | (generic verdict) | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Crypren | 3.51 |
| 8 | (generic verdict) | Trojan-Ransom.MSIL.Encoder | 3.02 |
| 9 | PolyRansom/VirLock | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.PolyRansom / Virus.Win32.PolyRansom | 2.96 |
| 10 | (generic verdict) | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Instructions | 2.69 |
* Statistics are based on detection verdicts of Kaspersky products. The information was provided by Kaspersky product users who consented to provide statistical data.
** Unique Kaspersky users attacked by specific ransomware Trojan families as a percentage of all unique users attacked by ransomware Trojans.
Miners
Number of new miner modifications
In Q2 2022, Kaspersky solutions detected 40,788 new modifications of miners. A vast majority of these (more than 35,000) were detected in June. Thus, the spring depression — in March through May we found a total of no more than 10,000 new modifications — was followed by a record of sorts.
https://e.infogram.com/_/vZm5Z2G3sFuuIAqZGWRA?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Number of new miner modifications, Q2 2022 (download)
Number of users attacked by miners
In Q2, we detected attacks using miners on the computers of 454,385 unique users of Kaspersky products and services worldwide. We are seeing a reverse trend here: miner attacks have gradually declined since the beginning of 2022.
https://e.infogram.com/_/ibd7ASo3u4ZaWhgBgbcF?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Number of unique users attacked by miners, Q2 2022 (download)
Geography of miner attacks
https://e.infogram.com/_/e5HYDOqPpDYZ08UMSsAM?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Geography of miner attacks, Q2 2022 (download)
TOP 10 countries and territories attacked by miners
| Country or territory* | %** | |
| 1 | Rwanda | 2.94 |
| 2 | Ethiopia | 2.67 |
| 3 | Tajikistan | 2.35 |
| 4 | Tanzania | 1.98 |
| 5 | Kyrgyzstan | 1.94 |
| 6 | Uzbekistan | 1.88 |
| 7 | Kazakhstan | 1.84 |
| 8 | Venezuela | 1.80 |
| 9 | Mozambique | 1.68 |
| 10 | Ukraine | 1.56 |
* Excluded are countries and territories with relatively few users of Kaspersky products (under 50,000).
** Unique users attacked by miners as a percentage of all unique users of Kaspersky products in the country.
Vulnerable applications used by criminals during cyberattacks
Quarterly highlights
During Q2 2022, a number of major vulnerabilities were discovered in the Microsoft Windows. For instance, CVE-2022-26809 critical error allows an attacker to remotely execute arbitrary code in a system using a custom RPC request. The Network File System (NFS) driver was found to contain two RCE vulnerabilities: CVE-2022-24491 and CVE-2022-24497. By sending a custom network message via the NFS protocol, an attacker can remotely execute arbitrary code in the system as well. Both vulnerabilities affect server systems with the NFS role activated. The CVE-2022-24521 vulnerability targeting the Common Log File System (CLFS) driver was found in the wild. It allows elevation of local user privileges, although that requires the attacker to have gained a foothold in the system. CVE-2022-26925, also known as LSA Spoofing, was another vulnerability found during live operation of server systems. It allows an unauthenticated attacker to call an LSARPC interface method and get authenticated by Windows domain controller via the NTLM protocol. These vulnerabilities are an enduring testament to the importance of timely OS and software updates.
Most of the network threats detected in Q2 2022 had been mentioned in previous reports. Most of those were attacks that involved brute-forcing access to various web services. The most popular protocols and technologies susceptible to these attacks include MS SQL Server, RDP and SMB. Attacks that use the EternalBlue, EternalRomance and similar exploits are still popular. Exploitation of Log4j vulnerability (CVE-2021-44228) is also quite common, as the susceptible Java library is often used in web applications. Besides, the Spring MVC framework, used in many Java-based web applications, was found to contain a new vulnerability CVE-2022-22965 that exploits the data binding functionality and results in remote code execution. Finally, we have observed a rise in attacks that exploit insecure deserialization, which can also result in access to remote systems due to incorrect or missing validation of untrusted user data passed to various applications.
Vulnerability statistics
Exploits targeting Microsoft Office vulnerabilities grew in the second quarter to 82% of the total. Cybercriminals were spreading malicious documents that exploited CVE-2017-11882 and CVE-2018-0802, which are the best-known vulnerabilities in the Equation Editor component. Exploitation involves the component memory being damaged and a specially designed script, run on the target computer. Another vulnerability, CVE-2017-8570, allows downloading and running a malicious script when opening an infected document, to execute various operations in a vulnerable system. The emergence of CVE-2022-30190or Follina vulnerability also increased the number of exploits in this category. An attacker can use a custom malicious document with a link to an external OLE object, and a special URI scheme to have Windows run the MSDT diagnostics tool. This, in turn, combined with a special set of parameters passed to the victim’s computer, can cause an arbitrary command to be executed — even if macros are disabled and the document is opened in Protected Mode.
https://e.infogram.com/_/1dqpsnMqrH26rdzDOOht?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Distribution of exploits used by cybercriminals, by type of attacked application, Q2 2022 (download)
Attempts at exploiting vulnerabilities that affect various script engines and, specifically, browsers, dipped to 5%. In the second quarter, a number of critical RCE vulnerabilities were discovered in various Google Chrome based browsers: CVE-2022-0609, CVE-2022-1096, and CVE-2022-1364. The first one was found in the animation component; it exploits a Use-After-Free error, causing memory damage, which is followed by the attacker creating custom objects to execute arbitrary code. The second and third vulnerabilities are Type Confusion errors associated with the V8 script engine; they also can result in arbitrary code being executed on a vulnerable user system. Some of the vulnerabilities discovered were found to have been exploited in targeted attacks, in the wild. Mozilla Firefox was found to contain a high-risk Use-After-Free vulnerability, CVE-2022-1097, which appears when processing NSSToken-type objects from different streams. The browser was also found to contain CVE-2022-28281, a vulnerability that affects the WebAuthn extension. A compromised Firefox content process can write data out of bounds of the parent process memory, thus potentially enabling code execution with elevated privileges. Two further vulnerabilities, CVE-2022-1802 and CVE-2022-1529, were exploited in cybercriminal attacks. The exploitation method, dubbed “prototype pollution”, allows executing arbitrary JavaScript code in the context of a privileged parent browser process.
As in the previous quarter, Android exploits ranked third in our statistics with 4%, followed by exploits of Java applications, the Flash platform, and PDF documents, each with 3%.
Attacks on macOS
The second quarter brought with it a new batch of cross-platform discoveries. For instance, a new APT group Earth Berberoka (GamblingPuppet) that specializes in hacking online casinos, uses malware for Windows, Linux, and macOS. The TraderTraitor campaign targets cryptocurrency and blockchain organizations, attacking with malicious crypto applications for both Windows and macOS.
TOP 20 threats for macOS
| Verdict | %* | |
| 1 | AdWare.OSX.Amc.e | 25.61 |
| 2 | AdWare.OSX.Agent.ai | 12.08 |
| 3 | AdWare.OSX.Pirrit.j | 7.84 |
| 4 | AdWare.OSX.Pirrit.ac | 7.58 |
| 5 | AdWare.OSX.Pirrit.o | 6.48 |
| 6 | Monitor.OSX.HistGrabber.b | 5.27 |
| 7 | AdWare.OSX.Agent.u | 4.27 |
| 8 | AdWare.OSX.Bnodlero.at | 3.99 |
| 9 | Trojan-Downloader.OSX.Shlayer.a | 3.87 |
| 10 | Downloader.OSX.Agent.k | 3.67 |
| 11 | AdWare.OSX.Pirrit.aa | 3.35 |
| 12 | AdWare.OSX.Pirrit.ae | 3.24 |
| 13 | Backdoor.OSX.Twenbc.e | 3.16 |
| 14 | AdWare.OSX.Bnodlero.ax | 3.06 |
| 15 | AdWare.OSX.Agent.q | 2.73 |
| 16 | Trojan-Downloader.OSX.Agent.h | 2.52 |
| 17 | AdWare.OSX.Bnodlero.bg | 2.42 |
| 18 | AdWare.OSX.Cimpli.m | 2.41 |
| 19 | AdWare.OSX.Pirrit.gen | 2.08 |
| 20 | AdWare.OSX.Agent.gen | 2.01 |
* Unique users who encountered this malware as a percentage of all users of Kaspersky security solutions for macOS who were attacked.
As usual, the TOP 20 ranking for threats detected by Kaspersky security solutions for macOS users is dominated by various adware. AdWare.OSX.Amc.e, also known as Advanced Mac Cleaner, is a newcomer and already a leader, found with a quarter of all attacked users. Members of this family display fake system problem messages, offering to buy the full version to fix those. It was followed by members of the AdWare.OSX.Agent and AdWare.OSX.Pirrit families.
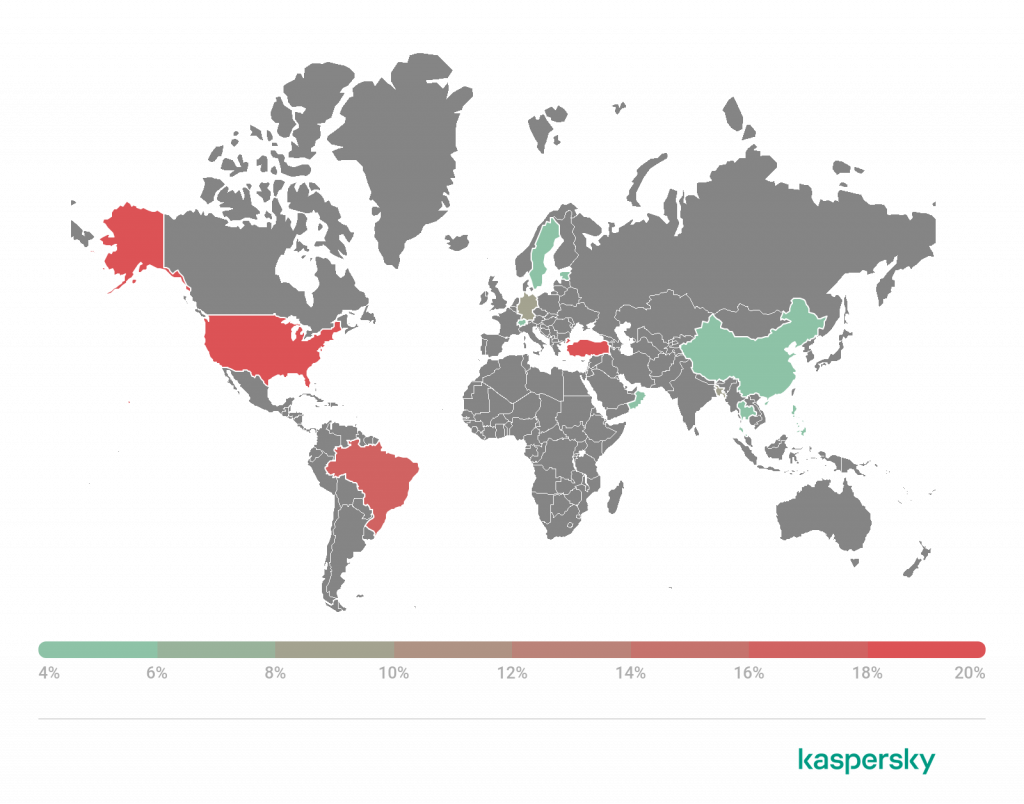
Geography of threats for macOS
https://e.infogram.com/_/sREMxK7Q3GvfvQe7t1Ql?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Geography of threats for macOS, Q2 2022 (download)
TOP 10 countries and territories by share of attacked users
| Country or territory* | %** | |
| 1 | France | 2.93 |
| 2 | Canada | 2.57 |
| 3 | Spain | 2.51 |
| 4 | United States | 2.45 |
| 5 | India | 2.24 |
| 6 | Italy | 2.21 |
| 7 | Russian Federation | 2.13 |
| 8 | United Kingdom | 1.97 |
| 9 | Mexico | 1.83 |
| 10 | Australia | 1.82 |
* Excluded from the rating are countries and territories with relatively few users of Kaspersky security solutions for macOS (under 10,000).
** Unique users attacked as a percentage of all users of Kaspersky security solutions for macOS in the country.
In Q2 2022, the country where the most users were attacked was again France (2.93%), followed by Canada (2.57%) and Spain (2.51%). AdWare.OSX.Amc.e was the most common adware encountered in these three countries.
IoT attacks
IoT threat statistics
In Q2 2022, most devices that attacked Kaspersky traps did so using the Telnet protocol, as before.
| Telnet | 82,93% |
| SSH | 17,07% |
Distribution of attacked services by number of unique IP addresses of attacking devices, Q2 2022
The statistics for working sessions with Kaspersky honeypots show similar Telnet dominance.
| Telnet | 93,75% |
| SSH | 6,25% |
Distribution of cybercriminal working sessions with Kaspersky traps, Q2 2022
TOP 10 threats delivered to IoT devices via Telnet
| Verdict | %* | |
| 1 | Backdoor.Linux.Mirai.b | 36.28 |
| 2 | Trojan-Downloader.Linux.NyaDrop.b | 14.66 |
| 3 | Backdoor.Linux.Mirai.ek | 9.15 |
| 4 | Backdoor.Linux.Mirai.ba | 8.82 |
| 5 | Trojan.Linux.Agent.gen | 4.01 |
| 6 | Trojan.Linux.Enemybot.a | 2.96 |
| 7 | Backdoor.Linux.Agent.bc | 2.58 |
| 8 | Trojan-Downloader.Shell.Agent.p | 2.36 |
| 9 | Trojan.Linux.Agent.mg | 1.72 |
| 10 | Backdoor.Linux.Mirai.cw | 1.45 |
* Share of each threat delivered to infected devices as a result of a successful Telnet attack out of the total number of delivered threats.
Detailed IoT-threat statistics are published in the DDoS report for Q2 2022.
Attacks via web resources
The statistics in this section are based on Web Anti-Virus, which protects users when malicious objects are downloaded from malicious/infected web pages. Cybercriminals create these sites on purpose; they can infect hacked legitimate resources as well as web resources with user-created content, such as forums.
TOP 10 countries and territories that serve as sources of web-based attacks
The following statistics show the distribution by country or territory of the sources of Internet attacks blocked by Kaspersky products on user computers (web pages with redirects to exploits, sites hosting malicious programs, botnet C&C centers, etc.). Any unique host could be the source of one or more web-based attacks.
To determine the geographic source of web attacks, the GeoIP technique was used to match the domain name to the real IP address at which the domain is hosted.
In Q2 2022, Kaspersky solutions blocked 1,164,544,060 attacks launched from online resources across the globe. A total of 273,033,368 unique URLs were recognized as malicious by Web Anti-Virus components.
https://e.infogram.com/_/Mii35djEPWnjaHq4c2Ve?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Distribution of web-attack sources by country and territory, Q2 2022 (download)
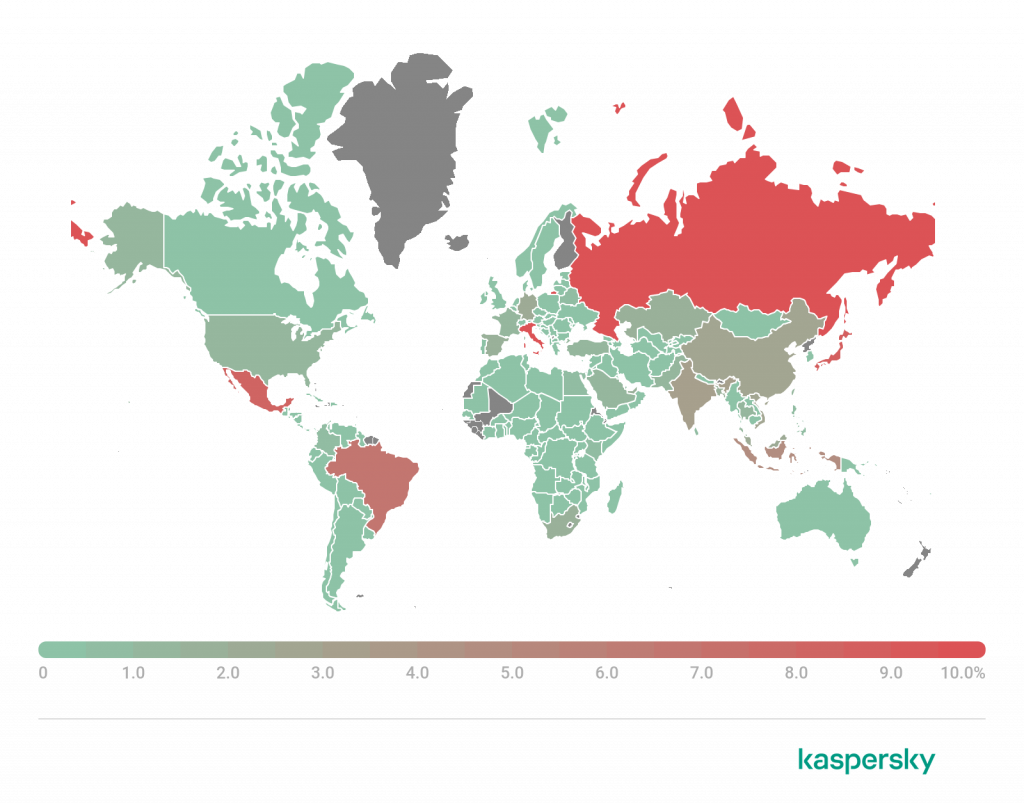
Countries and territories where users faced the greatest risk of online infection
To assess the risk of online infection faced by users around the world, for each country or territory we calculated the percentage of Kaspersky users on whose computers Web Anti-Virus was triggered during the quarter. The resulting data provides an indication of the aggressiveness of the environment in which computers operate in different countries and territories.
Note that these rankings only include attacks by malicious objects that fall under the Malware class; they do not include Web Anti-Virus detections of potentially dangerous or unwanted programs, such as RiskTool or adware.
| Country or territory* | %** | |
| 1 | Taiwan | 26.07 |
| 2 | Hong Kong | 14.60 |
| 3 | Algeria | 14.40 |
| 4 | Nepal | 14.00 |
| 5 | Tunisia | 13.55 |
| 6 | Serbia | 12.88 |
| 7 | Sri Lanka | 12.41 |
| 8 | Albania | 12.21 |
| 9 | Bangladesh | 11.98 |
| 10 | Greece | 11.86 |
| 11 | Palestine | 11.82 |
| 12 | Qatar | 11.50 |
| 13 | Moldova | 11.47 |
| 14 | Yemen | 11.44 |
| 15 | Libya | 11.34 |
| 16 | Zimbabwe | 11.15 |
| 17 | Morocco | 11.03 |
| 18 | Estonia | 11.01 |
| 19 | Turkey | 10.75 |
| 20 | Mongolia | 10.50 |
* Excluded are countries and territories with relatively few Kaspersky users (under 10,000).
** Unique users targeted by Malware-class attacks as a percentage of all unique users of Kaspersky products in the country.
On average during the quarter, 8.31% of the Internet users’ computers worldwide were subjected to at least one Malware-class web attack.
https://e.infogram.com/_/ZeKtZKpRpQBrBYKAEvcg?parent_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsecurelist.com%2Fit-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics%2F107133%2F&src=embed#async_embed
Geography of web-based malware attacks, Q2 2022 (download)
Local threats
In this section, we analyze statistical data obtained from the OAS and ODS modules of Kaspersky products. It takes into account malicious programs that were found directly on users’ computers or removable media connected to them (flash drives, camera memory cards, phones, external hard drives), or which initially made their way onto the computer in non-open form (for example, programs in complex installers, encrypted files, etc.).
In Q2 2022, our File Anti-Virus detected 55,314,176 malicious and potentially unwanted objects.
Countries and territories where users faced the highest risk of local infection
For each country, we calculated the percentage of Kaspersky product users on whose computers File Anti-Virus was triggered during the reporting period. These statistics reflect the level of personal computer infection in different countries and territories.
Note that these rankings only include attacks by malicious programs that fall under the Malware class; they do not include File Anti-Virus triggerings in response to potentially dangerous or unwanted programs, such as RiskTool or adware.
| Country or territory* | %** | |
| 1 | Turkmenistan | 47.54 |
| 2 | Tajikistan | 44.91 |
| 3 | Afghanistan | 43.19 |
| 4 | Yemen | 43.12 |
| 5 | Cuba | 42.71 |
| 6 | Ethiopia | 41.08 |
| 7 | Uzbekistan | 37.91 |
| 8 | Bangladesh | 37.90 |
| 9 | Myanmar | 36.97 |
| 10 | South Sudan | 36.60 |
| 11 | Syria | 35.60 |
| 12 | Burundi | 34.88 |
| 13 | Rwanda | 33.69 |
| 14 | Algeria | 33.61 |
| 15 | Benin | 33.60 |
| 16 | Tanzania | 32.88 |
| 17 | Malawi | 32.65 |
| 18 | Venezuela | 31.79 |
| 19 | Cameroon | 31.34 |
| 20 | Chad | 30.92 |
* Excluded are countries with relatively few Kaspersky users (under 10,000).
** Unique users on whose computers Malware-class local threats were blocked, as a percentage of all unique users of Kaspersky products in the country.
Source :
https://securelist.com/it-threat-evolution-in-q2-2022-non-mobile-statistics/107133/